Fig. 5. Calcium-regulated ER-PM MCSs.
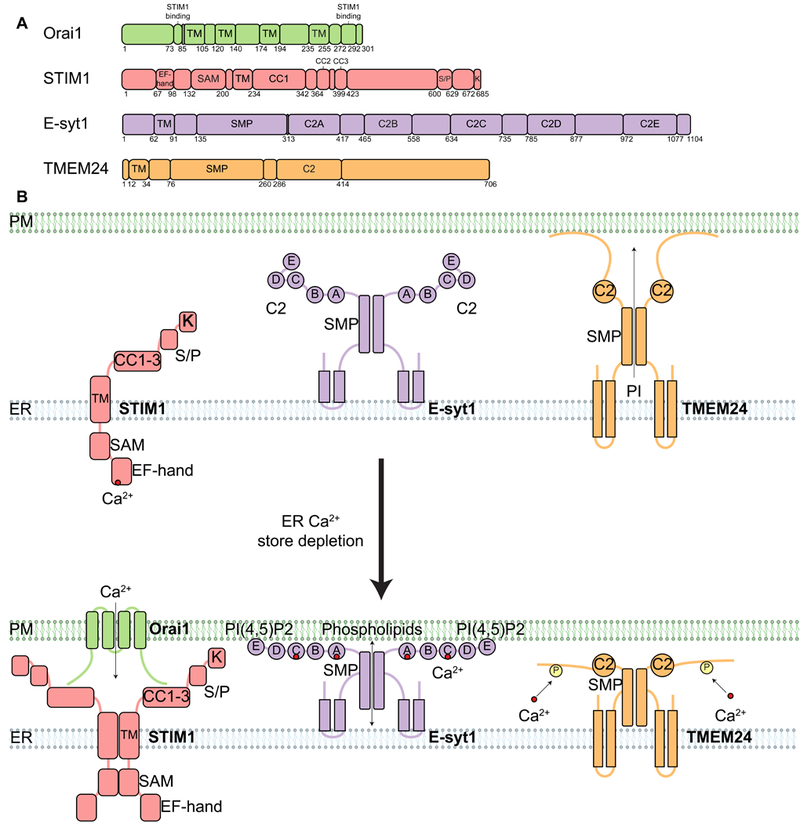
(A) Domain organization of proteins found at MCSs that are regulated by Ca2+. All examples are found at ER-PM MCSs. Relevant domains are indicated, including TM, EF-hand (binds Ca2+), C2 (binds Ca2+ and/or lipids), and SMP domains. SAM, sterile a motif; CC1 to CC3, coiled-coil domains 1 to 3; S/P, serine- and proline-enriched region; K, lysine-enriched region. (B) Diagram depicting the localization and oligomerization of ER MCS proteins that respond to calcium store depletion (compare top and bottom panels). The EF-hand domain of STIM1 is sensitive to calcium store depletion from the ER lumen, which leads to STIM1 oligomerization and translocation of STIM1 to ER-PM MCSs via its polybasic domain, allowing STIMI to bind and activate the Orail CRAC channel on the PM. Activation opens the Orail channel and funnels Ca2+ from the extracellular space back into the ER through the SERCA channel (not depicted). E-Syt1 is another ER membrane protein that translocates to ER-PM MCSs in response to ER calcium store depletion. E-Syt1 contains five C2 domains. ER calcium store depletion causes cytosolic Ca2+ to increase, the C2A and C2C domains bind this cytosolic Ca2+, and then C2E binds to PI(4,5)P2 at the PM, resulting in E-Syt1 translocation to ER-PM MCSs. E-Syt1 transfers phospholipids at ER-PM MCSs through the SMP domain. TMEM24 is an ER membrane protein with a C2 domain and an SMP domain. TMEM24 transfers PI from the ER to the PM through the SMP domain. However, ER calcium store depletion causes TMEM24 to bind Ca2+, become phosphorylated, and then dissociate from ER-PM MCSs.
