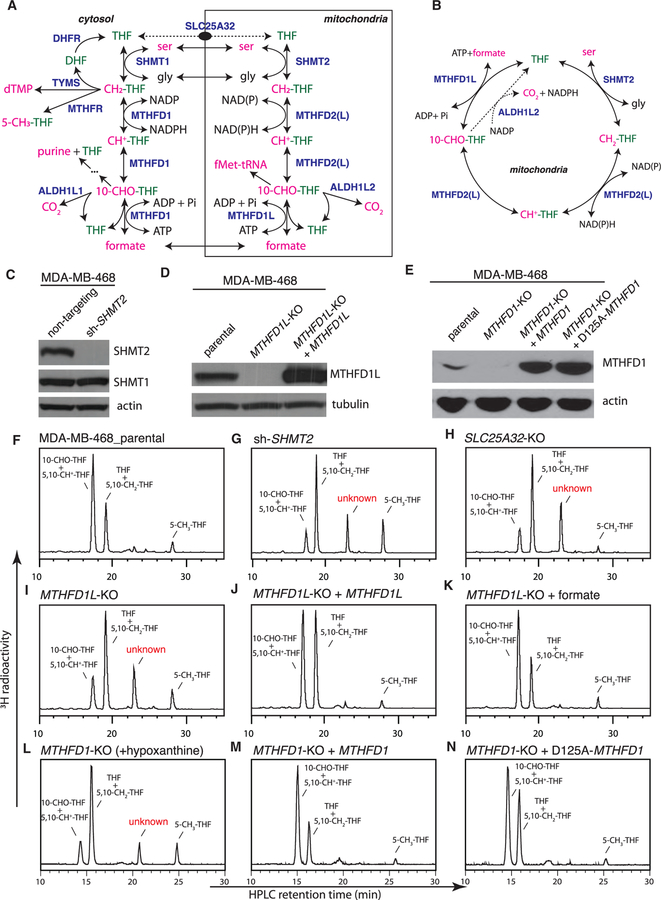
Figure 1. Formation of an Unusual Folate Metabolite in Mitochondrial-1C-Pathway-Deficient Cells.
(A) Compartmentation of mammalian 1C metabolism. SLC25A32 transports only the monoglutamate form of folates. In this intercompartmental cycle, 1C tends to flow clockwise, with serine oxidation in mitochondria and formate reduction in the cytosol.
(B) Folate-centered view of the mitochondrial 1C pathway.
(C) Western blot analysis of MDA-MB-468 cells stably expressing non-targeting or SHMT2-targeting short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs).
(D) Western blot analysis of MDA-MB-468 parental and MTHFD1L-knockout cells with or without ectopic expression of MTHFD1L.
(E) Western blot analysis of MDA-MB-468 parental and MTHFD1-knockout cells with or without ectopic expression of MTHFD1. The D125A mutation ablates the dehydrogenase and cyclohydrolase activity of MTHFD1.
(F–N) HPLC analysis of folates from isogenic MDA-MB-468 lines. ‘‘+ MTHFD1L’’ denotes ectopic MTHFD1L expression; ‘‘+ formate’’ denotes supplementing the labeling medium with 2 mM sodium formate; ‘‘+ hypoxanthine’’ denotes supplementing the labeling medium with 100 μM hypoxanthine, a necessity because the MTHFD1-knockout cells are purine auxotrophic. ‘‘+ MTHFD1’’ denotes ectopic MTHFD1 expression.
See also Figure S1.