Fig. 8.
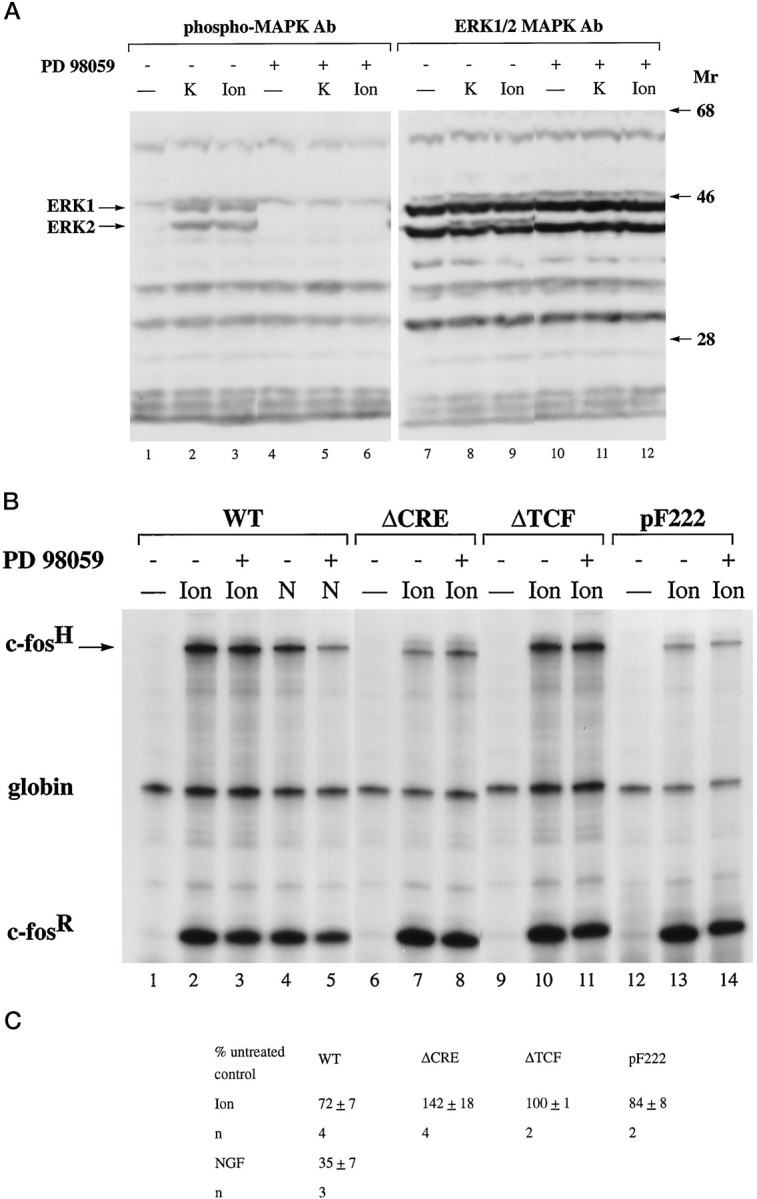
Effect of the MAP kinase kinase 1 inhibitor PD 98059 on MAP kinases/ERKs activation (A) and CRE-dependent and TCF-dependent calcium-activated transcription in PC12 cells (B, C). A, Immunoblot analysis of lysates from PC12 cells before (lanes 1, 4, 7, 10) and 5 min after either KCl stimulation (K; lanes 2, 5, 8, 11) or ionomycin treatment (Ion; lanes 3, 6, 9, 12), using antibodies specific for either phospho-MAP kinases/ERKs (lanes 1–6) or for MAP kinases/ERKs (lanes 7–12) to control for even protein loading. Treatment of the cells with 50 μm PD 98059 (lanes 4–6 and10–12) was done for 60 min before stimulation.Mr, Protein molecular weight standards (× 10−3). B, RNase protection analysis was performed as described in Figure 2. PC12 cells were transfected with plasmid pF711 (wild-type c-fosgene, lanes 1–5), pFosΔCRE (lanes 6–8), pFosΔTCF (lanes 9–11), and pF222 (lanes 12–14). RNA was isolated from unstimulated cells (lanes marked −) or cells stimulated with ionomycin (Ion) or NGF (N). Treatment of the cells with 50 μm PD 98059 (lanes 3, 5, 8, 11, 14) was done for 60 min before stimulation. Similar results were obtained with PD 98059 on KCl-induced TCF-dependent and CRE-dependent transcriptional activation (data not shown).C, Quantitation of RNase protection experiments by the PhosphorImager. The levels of c-fos mRNA transcribed from the indicated plasmids and normalized for transfection efficiency to the level of α-globin mRNA in cells treated with PD 98059 are expressed as a percentage of the amount of c-fos mRNA, normalized to α-globin expression, produced by untreated cells in response to the same stimulus. The mean ± SEM is shown.
