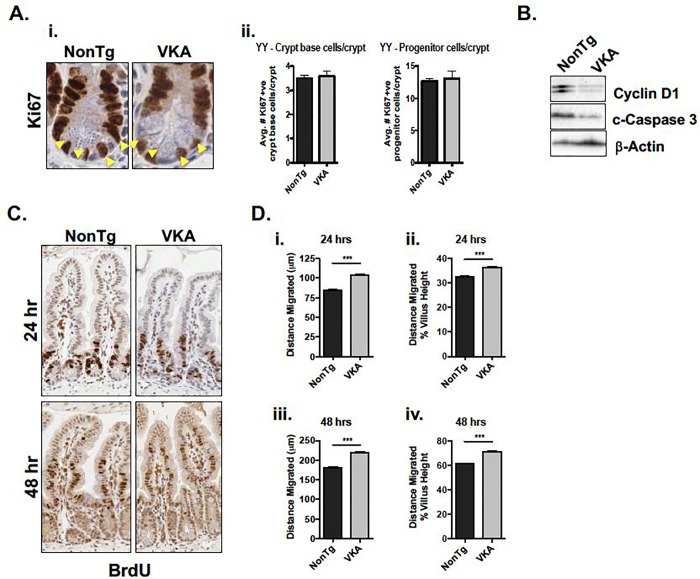
Fig 4. Intestinal epithelial cell repair mechanisms are altered prior to inflammation onset in 12-week old VKA mice.
(A-i) VKA mice do not demonstrate a change in number of Ki67-positive cells. Yellow arrowheads denote crypt base cells. (A-ii) Ki67-positive cells from 100 open crypts (n = 5 mice/genotype) were quantified. Crypt base cells were scored by counting the number of Ki67-positive cells in the bottom third of the crypt. The remaining cells were scored as progenitor cells. (B) Proliferation marker Cyclin D1 and apoptotic marker cleaved (c-) Caspase 3 are both decreased in VKA mice. (C, D) VKA mice show increased migration of epithelial cells up the crypt-villus axis relative to their NonTg counterparts, as demonstrated by IHC (C), and quantified by measuring the distance of the furthest-migrated BrdU-positive cell (~ 100 villi from 3 mice/genotype) (D). (D-i, -iii) Distance migrated was quantified by measuring the distance from the base of the crypt, to the furthest positively BrdU-labelled cell. (D-ii, iv) To correct for possible differences in villus height, the average distance migrated was normalized to the average villus height. Representative plots of at least three blind measurements are shown. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired student’s t-test. ***p<0.001, error bars represent SEM.