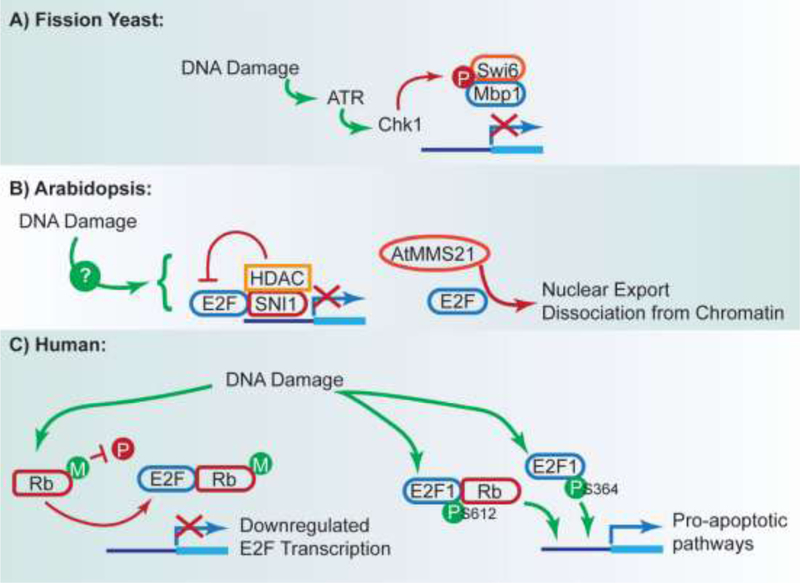
Figure 3: Summary of Transcriptional Responses to DNA Damage.
A) In fission yeast, MBF transcription is phosphorylated by Chk1 in response to DNA damage, leading to decreased transcription. B) Studies in Arabidopsis indicate that E2F transcription is regulated by a variety of pathways. SNI1 has been demonstrated to decrease E2F transcription by recruiting HDAC. In addition, AtMMS21 reduces E2F chromatin binding and nuclear translocation. C) In humans, DNA damage results in diversification of E2F species. Rb methylation interferes with its phosphorylation, resulting in continued sequestration of E2F and reduced E2F transcription. Conversely, specific phosphorylated E2F1 species, with or without Rb are induced by DNA damage and upregulate pro-apoptotic pathways.