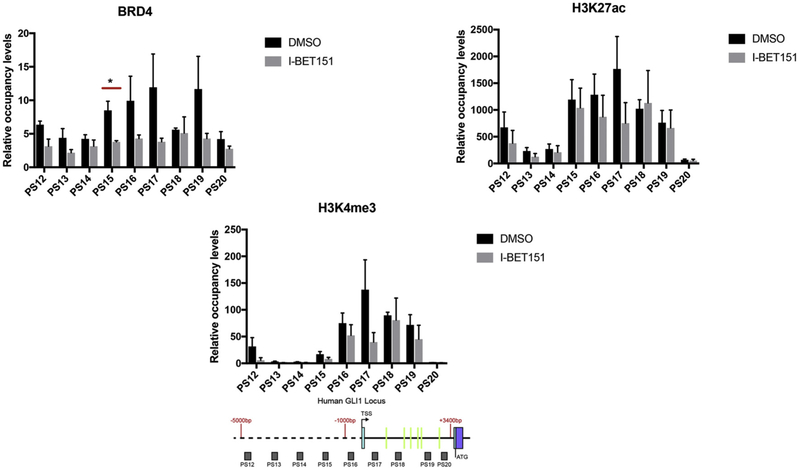
Fig. 5.
BRD4 occupancy is reduced with treatment by I-BET151 in the human GLI1 locus. Brd4, H3K27ac and H3K4me3 occupancy were analyzed by ChIP-quantitative PCR in BL1648 (human Burkitt lymphoma cells not dependent on SHH signaling) cells treated with 1μM I-BET151 for 24 h. The signals were normalized to a control ChIP performed using rabbit IgG. I-BET151 (an inhibitor of bromodomain end terminal protein) reduces BRD4 without changing active chromatin mark occupancy in the first intron of the human GLI1 locus. Error bars represent the S.E. of three independent experiments, unless otherwise indicated. p values ≤ 0.05 are considered statistically significant and indicated by an asterisk. (Below) A schematic of the human GLI1 locus from −5,000 nt to + 3700 nt, relative to the transcription start site (TSS) is shown. The probe sets (PS) PS12-PS20 are represented as shaded boxes (sequences in Methods section). 5′ - > 3′ is left to right. Green lines in the intron represent the locations of the human GBS.