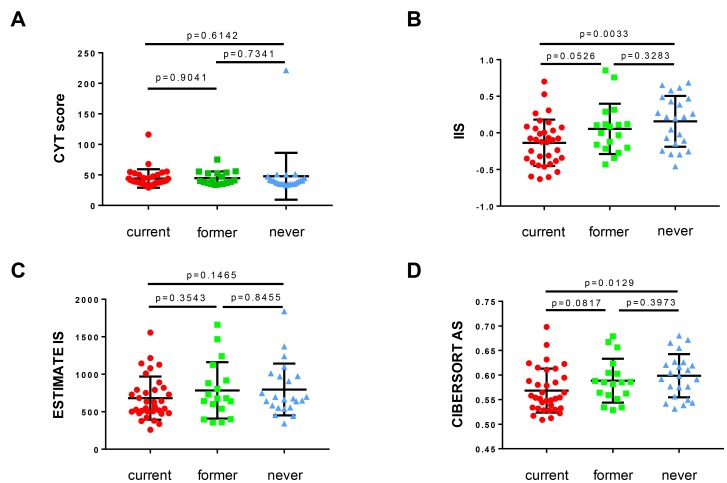
Figure 1. The association of smoking history with immune infiltration and T cell activation in non-cancerous bronchial epithelium demonstrates stepwise immunosuppression with increasing smoking history.
Human bronchial mucosa samples (total n = 75, current smoker n = 34, former smoker n = 18, never smoker n = 23; clinical and expression data from [24]); (A) CYT score, (B) IIS, (C) ESTIMATE IS, and (D) CIBERSORT AS illustrated as scatter blots for current, former and never smokers. For all statistical analyses, a Mann-Whitney-U test was used (α = 0.05) and p-values ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant. CYT score – cytolytic activity score; IIS – immune infiltration score; ESTIMATE IS – ESTIMATE signature score; CIBERSORT AS – CIBERSORT absolute score; current – current smoker (red dots); former – former smoker (green squares); never – never smoker (blue triangles).