Figure 3. STIL S428 phosphorylation promotes centriole duplication.
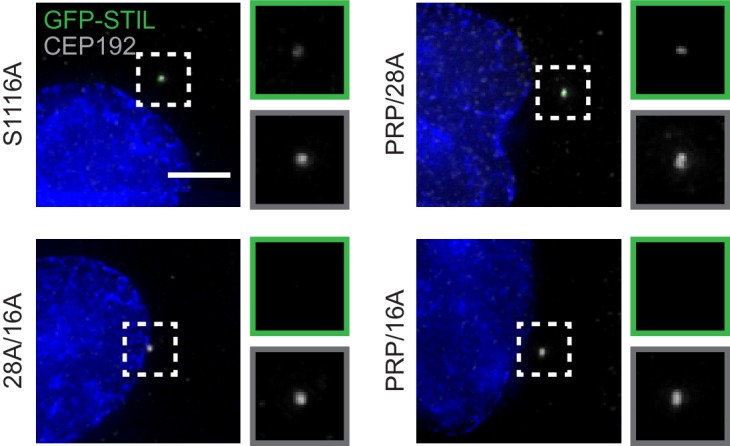
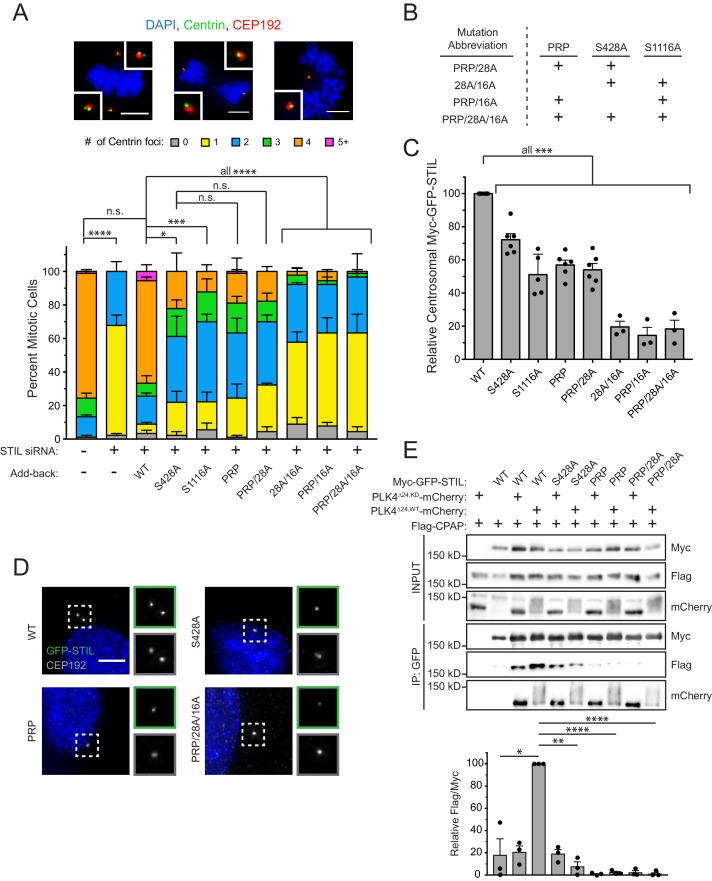
(A) Quantification showing the number of mitotic Centrin foci in cells that were depleted of endogenous STIL and induced to express a siRNA-resistant Myc-GFP-STIL transgene as indicated. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean across three independent experiments. Representative images show example mitotic cells. Scale bars represent 5 µm. (B) The table shows abbreviations for Myc-GFP-STIL transgenes with multiple mutations. ‘PRP’ represents a triple mutation of P404A, R405A, and P408A. (C) Quantification of the relative centrosomal levels of Myc-GFP-STIL constructs from (A) in S/G2 phase cells with at least 40 cells measured per experiment. Bars represent the mean of at least three independent experiments with the average within each experiment shown as a dot. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (D) Representative images of data shown in (C). Scale bar represents 5 µm. (E) HEK293FT cells were transfected with the indicated constructs and subjected to co-immunoprecipitation and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Graph represents the mean of relative levels of immunoprecipitated Flag/Myc signal across three independent experiments. A dot displays measurement from each experiment. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between measurements (*: p<0.05; **: p<0.005; ***: p<0.0005; ****: p<0.0001). For Figure 3A, statistics were calculated using an unpaired t-test against the fraction of cells containing less than four centrioles in mitosis. For Figure 3C and E, statistics were calculated using a one-sample t-test where mean values were tested as being different from a value of 100.
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. STIL transgenes are expressed to similar levels.
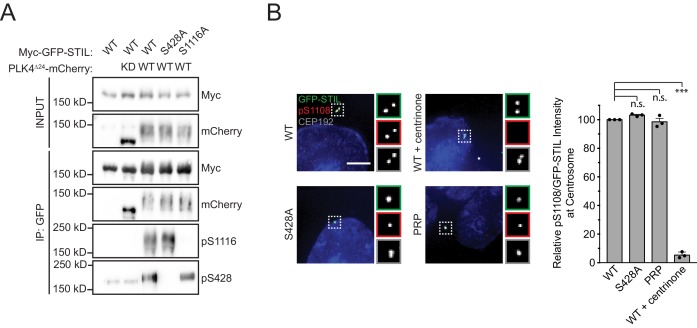
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. The STIL PRP mutations do not affect STIL S428 phosphorylation.
Figure 3—figure supplement 3. Preventing STIL phosphorylation reduces the accumulation of STIL at the centriole.