Figure 5. Engineering biohybrid robots.
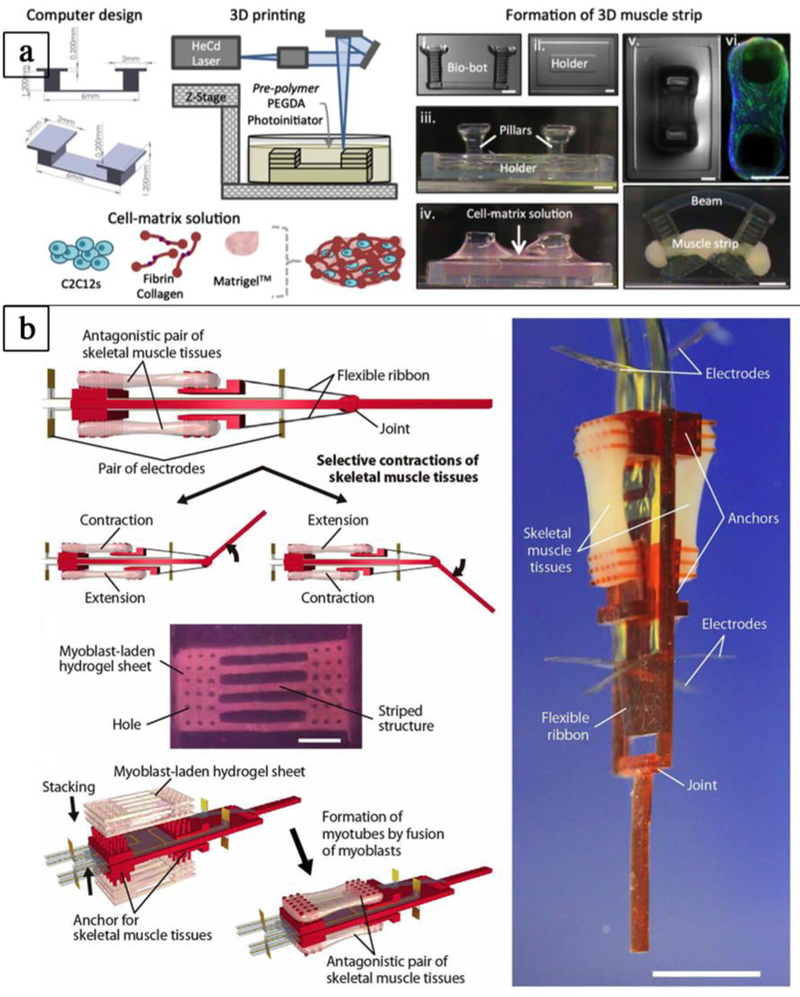
a-b) Assembling of biohybrid robots combining rapid prototyping techniques and living cells. a) 3D printed hydrogel “bio-bots” with an asymmetric physical design and powered by the actuation of an engineered mammalian skeletal muscle strip (adapted with permission from [101] ©2014 PNAS). b) Biohybrid robot powered by an antagonistic pair of skeletal muscle tissues (adapted with permission from Morimoto et al.[102] ©2018 American Association for the Advancement of Science).
