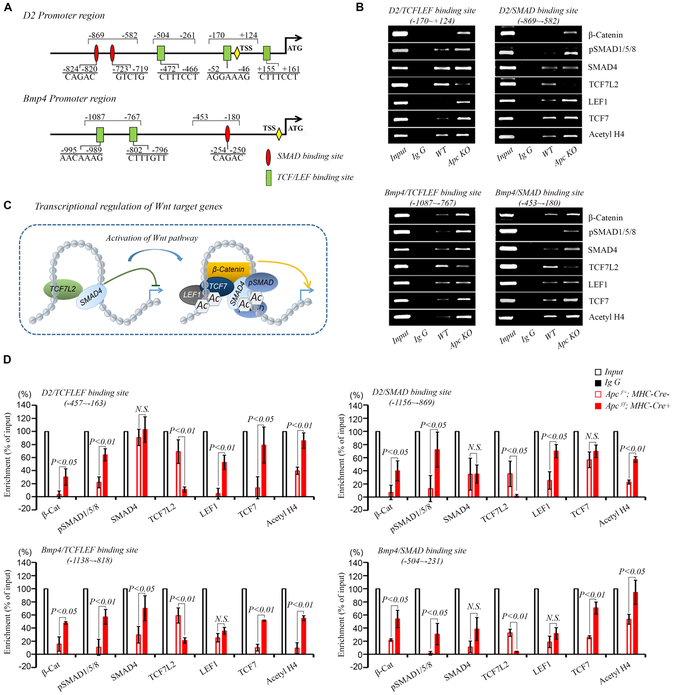
Figure 5. Wnt nuclear effectors are recruited to the regulatory element of Cyclin D2 and Bmp4 promoters.
A, Amplicon positions and putative TCF/LEF and SMAD binding sites relative to transcription start site (TSS). B, ChIP shows that the recruitments of β-catenin, Smad4, pSmad1/5/8, Lef1 and Tcf7 to the TCF/LEF and SMAD binding sites in the Cyclin D2 and Bmp4 promoters are increased, while Tcf7l2 is removed from these regions in Apc cKO compared to WT hearts at E17.5. These changes are accompanied by an increase in histone H4 acetylation (Acetyl H4), indicating transcriptional activation. Inputs are 2% of total mount chromatin. C, A diagram shows Wnt target gene regulation. In WT mice, Tcf7l2 interacts with SMAD family members to suppress gene transcription. Upon Apc deletion, Tcf7l2 is removed from TCF/LEF binding sites and replaced with activating forms of TCF/LEF family members, Tcf7 and Lef1 to promote the recruitment of pSmad1/5/8 and β-catenin as well as histone H4 acetylation. D, Semiquantitative analysis of the relative enrichment of proteins bound to the Tcf7l2 or SMAD consensus site. The intensity of each band in the gel images was measured using the ImageJ program and normalized by input. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of 4 independent experiments.