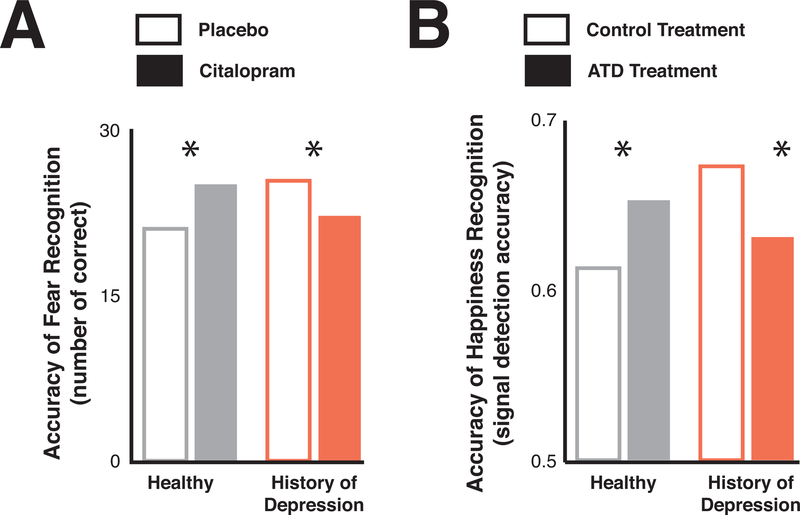
Figure 4: Serotonin differentially impacts emotional recognition dependent on individual differences.
A) The SSRI citalopram (filled bars), compared to placebo (open bars), causes a bidirectional effect on fear recognition depending on whether subjects had a history of depression (red bars; decreases fear recognition due to citalopram) or were healthy volunteers (grey bars; increases fear recognition due to citalopram). Reproduced and adapted with permission from(Bhagwagar et al., 2004). B) ATD (filled bars versus placebo open bars) causes a bidirectional effect on the recognition of happy emotions dependent on if subjects were healthy (left graph, grey bars, an increase due to ATD) or recovered depressed (right graph, red bars, a decrease due to ATD). Reproduced and adapted with permission from(Hayward et al., 2005).