Figure 5. Modular synthesis of full-length Oxytricha chromosomes.
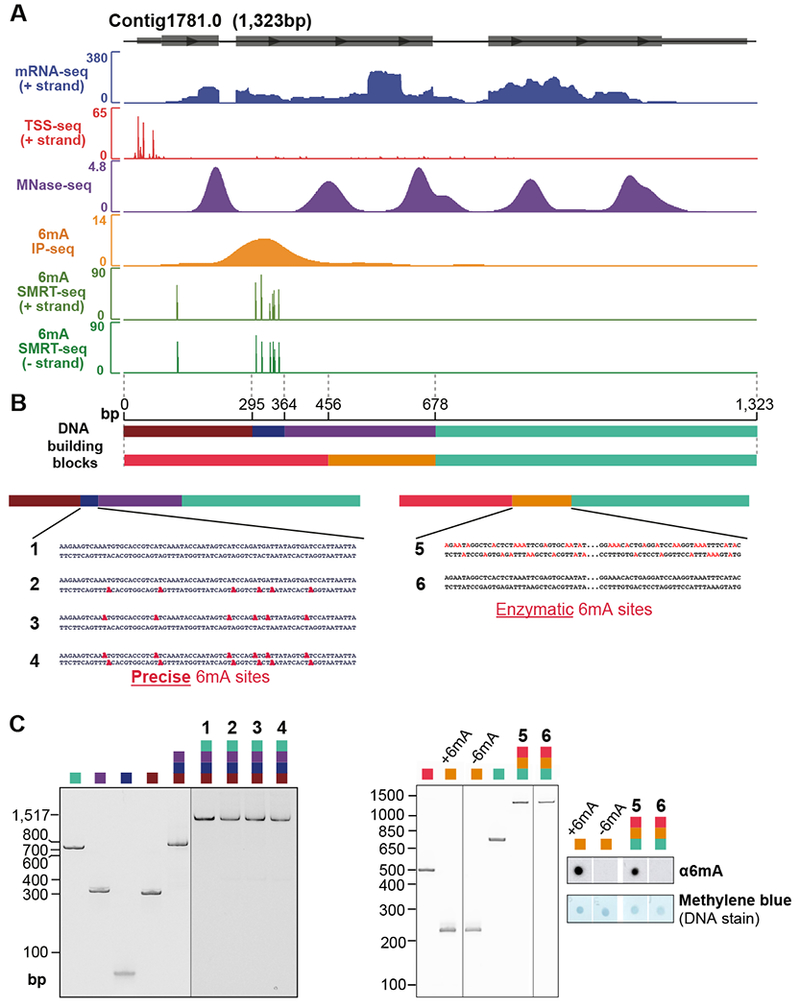
(A) Features of the chromosome selected for synthesis. Grey boxes represent exons. All data tracks represent normalized coverage except for SMRT-seq, which represents the confidence score [−10 log(p-value)] of detection of each methylated base.
(B) Schematic of chromosome construction. Different colors denote DNA building blocks ligated to form the full-length chromosome. Precise 6mA sites (bold red) represent cognate 6mA positions revealed by SMRT-seq in native genomic DNA. These are introduced via oligonucleotide synthesis. For chromosome 5, 6mA sites (non-bold red) represent possible locations ectopically installed by a bacterial 6mA methyltransferase, EcoGII. Intervening sequence within chromosomes 5 and 6 is represented as “…”
(C) Native polyacrylamide gel analysis and anti-6mA dot blot analysis of building blocks and purified synthetic chromosomes.
