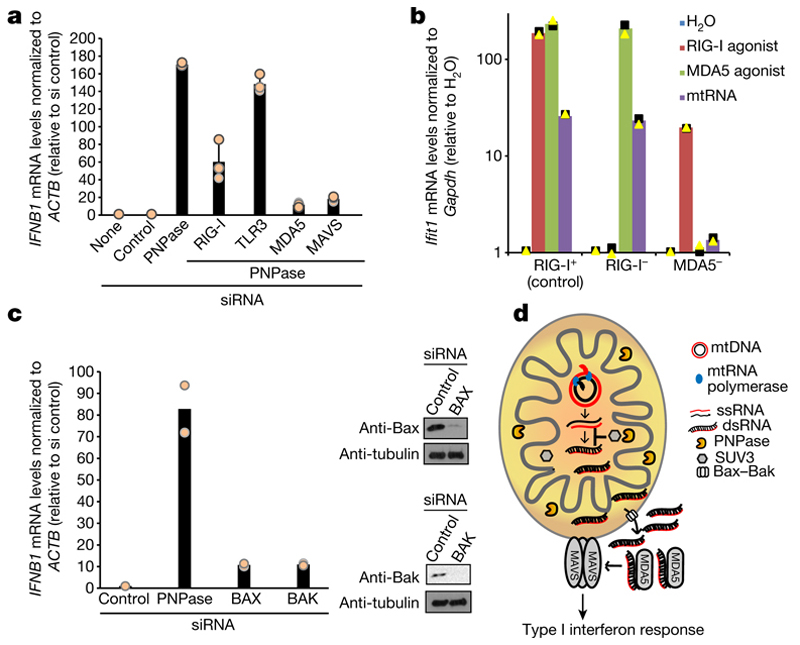
Fig. 4. MDA5 is the primary sensor of cytosolic mtdsRNA released in a Bax–Bak dependent fashion.
a, RT–qPCR analysis of IFNB1 expression in HeLa cells transfected with indicated siRNAs. Data are mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments. b, RT–qPCR analysis of Ifit1 expression in Ddx58+/− (control, RIG-I+), Ddx58−/− (RIG-I−) and Ifih1−/− (MDA5−) immortalized MEFs transfected with mtRNA, RIG-I (ppp-IVT-RNA99nt) or MDA5 (CIP-EMCV RNA) specific agonists. Data are the mean from two independent experiments. Values are plotted on a logarithmic scale. c, Left, RT–qPCR analysis of IFNB1 mRNA in HeLa cells treated with the indicated siRNAs. Data are mean from two independent experiments. Right, western blot of siRNA depletion efficiency. Blots are representative of two experiments. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1. d, Model of mtdsRNA suppression by the RNA degradosome. Loss of PNPase causes accumulation of mtdsRNA and release of mtdsRNA into the cytoplasm in a Bax–Bak dependent manner. PNPase restricts mtdsRNA in matrix (together with SUV3) and IMS. MDA5 acts as the primary mtdsRNA sensor transducing an interferon response through the MAVS signalling pathway.