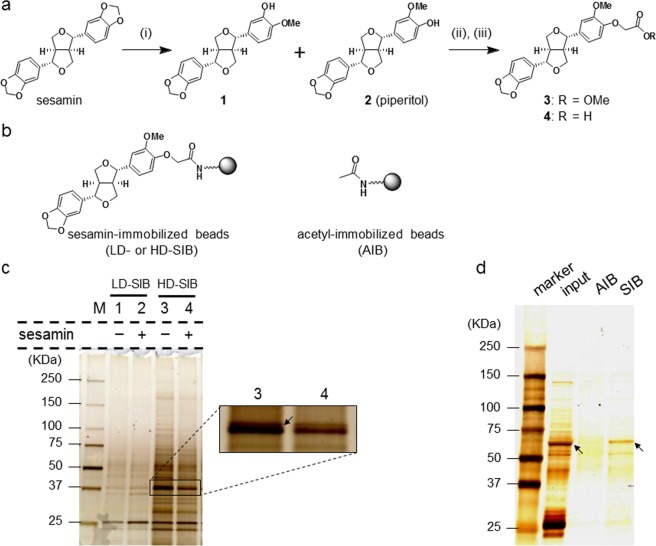
Figure 1.
Identification of Steroleosin B as a sesamin-binding protein and purification of recombinant GST-fused Steroleosin B. (a) Reaction conditions for the synthesis of sesamin probe 4; (i) DIBAL, toluene, reflux, 1 h; (ii) BrCH2CO2Me, K2CO3, DMF, rt, 1 h; (iii) 1 N NaOH aq., THF, rt, 1 h. (b) Structure of LD- or HD-SIB and AIB. (c) Lysates from sesame seedlings in the absence (lanes 1 and 3) or presence (lanes 2 and 4) of sesamin were incubated with LD-SIB (lanes 1 and 2) or HD-SIB (lanes 3 and 4). The proteins eluted from SIB were resolved using sodium dodecyl sulfate-poly acrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and were then subjected to silver staining. The band marked by the arrow (lane 3 in magnified image) was diminished in the presence of sesamin as a competitor (lane 4). (d) Whole cell extracts of E. coli producing recombinant GST-fused Steroleosin B were incubated with AIB or SIB. The resulting eluents were resolved using SDS-PAGE followed by silver staining. The arrows in SDS-PAGE show the bands for GST-fused Steroleosin B.