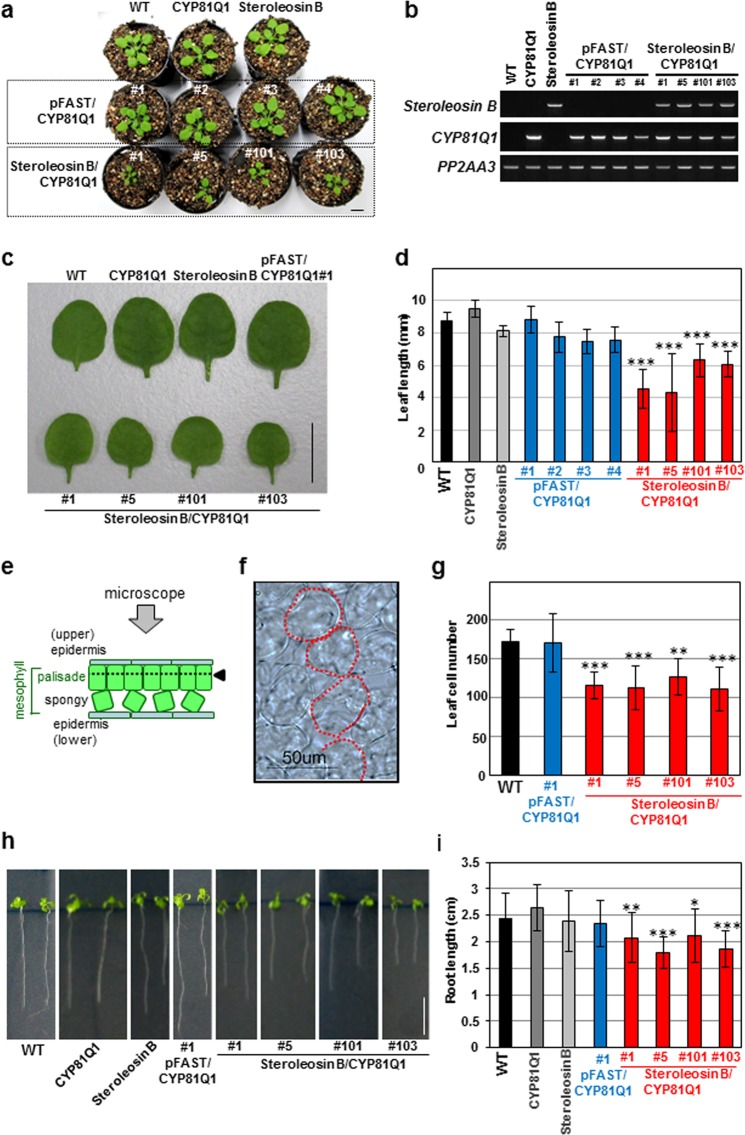
Figure 4.
Ectopic expression of Steroleosin B and CYP81Q1 genes in transgenic Arabidopsis plants suppress growth, leaf expansion and root elongation. (a) The rosettes of four-week-old wild-type and transgenic Pro35S:CYP81Q1, Pro35S:Steroleosin B, pFAST/Pro35S:CYP81Q1, and Pro35S:Steroleosin B/Pro35S:CYP81Q1 plants. (b) Expression of Steroleosin B and CYP81Q1 genes in wild-type, Pro35S:CYP81Q1, Pro35S:Steroleosin B and four T3 lines of pFAST/Pro35S:CYP81Q1 and Pro35S:Steroleosin B/Pro35S:CYP81Q1 plants. PP2AA3 was used as an internal control. (c) Morphology of the forth leaves of wild-type and transgenic Pro35S:CYP81Q1, Pro35S:Steroleosin B, pFAST/Pro35S:CYP81Q1, and Pro35S:Steroleosin B/Pro35S:CYP81Q1 plants. (d) The lengths of the fourth leaves of Arabidopsis plants (n = 8). (e) Model of a leaf cross-section indicating mesophyll palisade cells. The dotted lines marked by the arrowheads represent the focus plane of the microscopic observations in (f) and (g). (f) Image of mesophyll palisade cells under microscopic observation. Red lines indicate the outlines of palisade cells. The mesophyll palisade cells form a simple round shape (g) Numbers of mesophyll palisade cells along the longitudinal axes of fourth leaves of Arabidopsis plants (n = 8). (h) Images of the wild-type and transgenic Pro35S:CYP81Q1, Pro35S:Steroleosin B, pFAST/Pro35S:CYP81Q1 and Pro35S:Steroleosin B/Pro35S:CYP81Q1 plants used for measurement of root length in (g). (g) Lengths of main roots in Arabidopsis plants (n = 28–36). Bars = 1 cm in (a,c,h). Asterisks in (d,g,i) indicate significant differences relative to the wild-type (***P < 0.001. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05). One-way ANOVA was performed, followed by Dunnett’s test. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Error bars indicate standard deviations of indicated biological replicates.