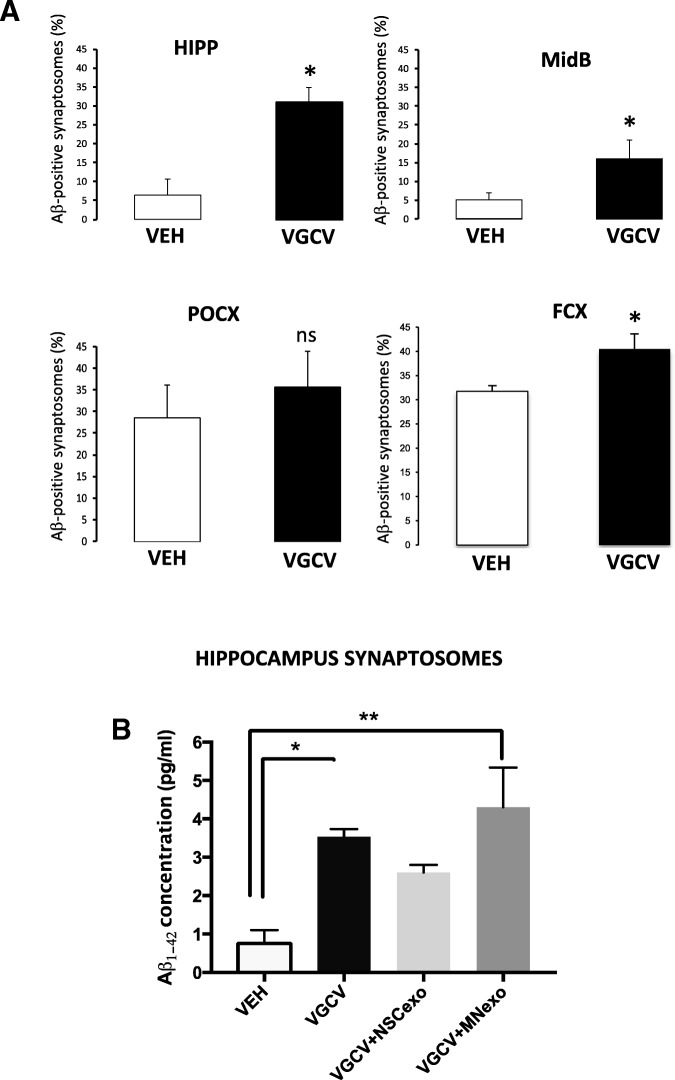
Fig. 8.
Hippocampal synaptic vulnerability to Aβo binding is increased in mice with ablated NSC and this increase is rescued by ICV injection of NSC-exo. a) Nestin-δ-HSV-Tk mice were fed vehicle or valganciclovir (VGCV) chow for 4 weeks. At the end of the 4 weeks, mice were euthanized and synaposomes were isolated from the hippocampus (HIPP), mid brain (MidB), frontal cortex (FCX) and parieto-occipital cortex (POCX) and challenged with Fluor 647-Aβ oligomers (2.5 μM) for 30 min. The percent of synaptosomes with bound Aβ was evaluated using flow cytometry. Mice treated with VGCV (with ablated NSC) showed a significant increase in the percent of Aβ positive synaptosomes as compared to vehicle-treated mice (with intact NSC) in the hippocampus, midbrain and frontal cortex. No statistically significant differences were noted in the parieto-occipital cortex. N = 6 mice/group. *p < 0.05 Student’s two-tailed T-test. b) Nestin-δ-HSV-Tk mice were fed vehicle or valganciclovir (VGCV) chow for 4 weeks. At the end of the 4 weeks, fresh hippocampal brain slices were prepared and treated with NSC-exo or MN-exo for 4 h before being challenged with Aβ oligomers (2.5 μM for 30 min). ELISA was used to measure the amount of Aβ bound to synaptosomes. N = 3 mice/group. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 one-way ANOVA (F = 7.276) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test