Figure 2.
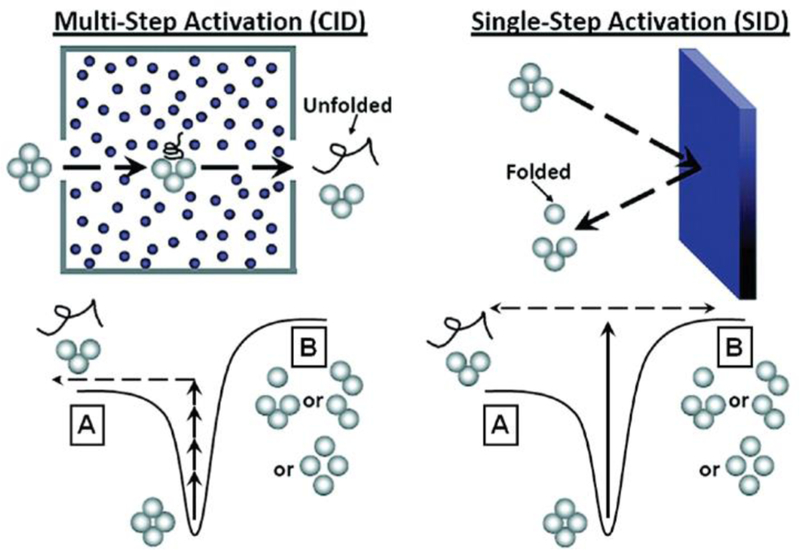
Simplified representation of the pathways a protein complex may take when undergoing CID (left) or SID (right). CID involves multiple low-energy collisions (top left) that generally result in dissociation via the lowest energy pathway (bottom left). SID involves a single-step, high energy deposition via collision with a surface (top right) and typically results in dissociation via alternative dissociation pathways and dissociation products form that are often compact and reflective of the native structure (bottom right). Reproduced from Zhou, M.; Wysocki, V.H., Surface induced dissociation: Dissecting noncovalent protein complexes in the gas-phase. Acc. Chem. Res., 47(4), 1010–1018. Copyright 2014 American Chemical Society.
