Table 1.
Performance of example HBV RNaseH inhibitors
| Compound | Formal Name | Structure | EC50 HBVa | CC50a | TIb | IC50 Human RNaseH1a | HSV-1 inhibitionc | MIC80 E. colid | MIC80 Staphylo-coccus spp.d | MIC80 C. neoformanse |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| αHT | ||||||||||
| 46 | β-Thujaplicinol | 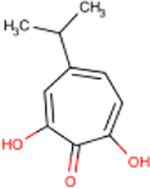 |
1.0 ± 0.6 | 25 ± 20 | 25 | 58 | 5 | 44 | 20 | 8 |
| 107 | CM1012–6b | 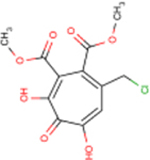 |
0.4 ± 0.2 | >80 | >200 | 221 | - | - | - | 50 |
| 280 | AG77 | 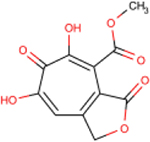 |
0.5 ± 0.1 | >77 | >154 | 177 | - | - | - | - |
| 336 | YA-I-78 | 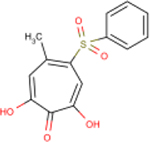 |
0.4 ± 0.2 | 45 ± 8 | 130 | 37 | + | - | 44 | - |
| HID | ||||||||||
| 1 | TRC 939800 | 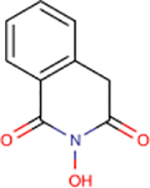 |
4.2 ± 1.4 | 75 ± 24 | 18 | 218 | - | - | - | - |
| 83 | MB88 | 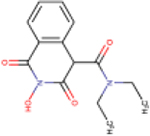 |
2.3 ± 1.6 | 100 ± 35 | 43 | 45 | - | - | - | ND |
| 86 | VS42 | 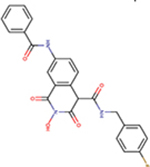 |
1.4 ± 0.3 | 99 ± 2 | 71 | 158 | - | - | ND | ND |
| 89 | VS51 | 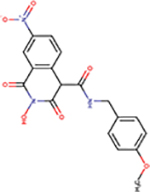 |
2.6 ± 0.8 | 28 ± 8 | 11 | 111 | - | ND | ND | ND |
| HPD | ||||||||||
| 208 | Sun B8155 | 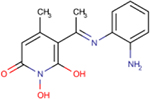 |
0.69 ± 0.2 | 15 ± 7 | 22 | 194 | - | - | - | ND |
| A23 | ARB-270496–1 | 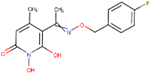 |
0.11 ± 0.01 | 10 ± 2 | 300 | 21 | - | - | ND | ND |
| A24 | ARB-270497–1 | 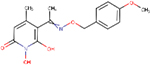 |
0.29 ± 0.1 | 31 ± 16 | 352 | 28 | - | - | ND | ND |
μM
CC50/EC50
Log10 reduction in viral titers at 5 μM; -, <10-fold reduction of titers at 5 μM; + >10-fold reduction in titer at 5 μM
Minimum inhibitory concentration 80% (MIC80) (μM); -, no inhibiton at 70 μM
MIC80 (μM); -, no inhibition of growth at 50 μM
Abbreviations: EC50; 50% effective concentration; CC50, 50% cytotoxic concentration; TI, therapeutic index; IC50, 50% inhibitory concentration; RNaseH1, ribonuclease H1; HSV, Herpes Simplex Virus;
MIC80, minimal 80% inhibitory concentration; E. coli, Escerichia coli; Spp., any of multiple species within a genus; αHT, α-Hydroxytropolones; HID, N-Hydroxyisoquinolinediones; HPD, N-Hydroxypyridinediones; ND, not determined.
