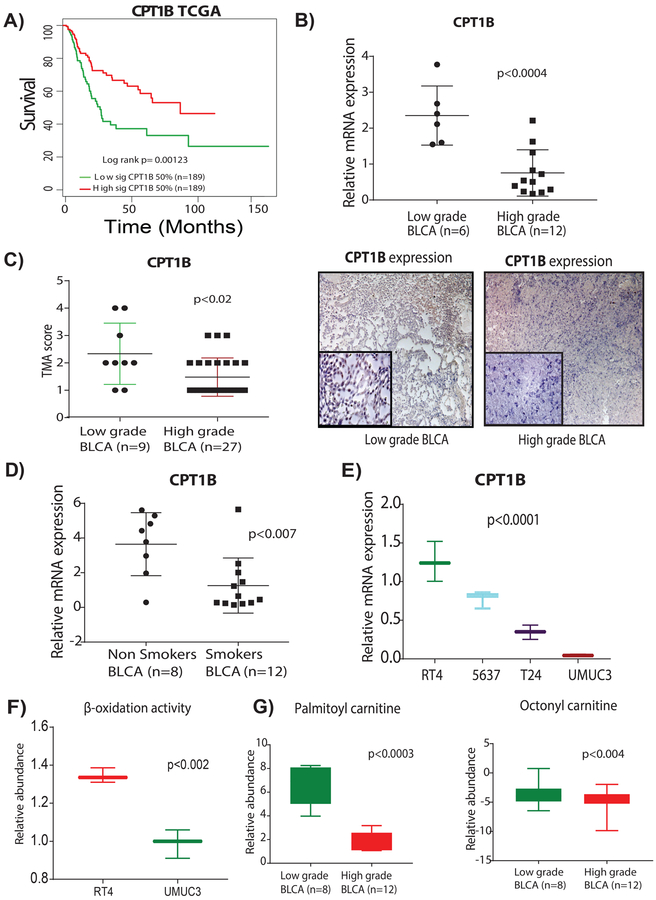
Figure 4. Suppression of CPT1B is associated with poor survival, low β-oxidation, and low levels of acylcarnitines in high-grade BLCA.
A) Low expression of CPT1B was associated with poor survival in TCGA cohort (log-rank p= 0.00123). B) Low CPT1B mRNA expression demonstrates the low CPT1B expression in high-grade BLCA (n=6 and n=12 low-grade and high-grades tissues respectively; p<0.0004. C) TMA analysis of BLCA patient tissues (n=9 and n=27, low-grade and high-grade respectively) shows a trend for lower intensity in the high-grade tissues (p<0.02). Immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis shows the low CPT1B protein levels in high-grade BLCA; on a scoring scale of 1–4, one is low intensity and 4 is the highest intensity of the CPT1B expression. D) mRNA expression analysis shows the low CPT1B expression in smokers with BLCA (n=8 and n=12 non-smokers and smokers respectively; p<0.007). E) mRNA expression analysis shows a gradual decrease of CPT1B levels with an increased grades of the BLCA in cell lines (p<0.0001). For all the mRNA measurements CPT1B levels were normalized to a GAPDH internal control. F) LC-MS based analysis using Biocrates AbsoluteIDQ p180 Kit shows the low β-oxidation activity in high-grade BLCA cell lines (p<0.02). G) LC-MS based analysis reveals low levels of palmitoyl (p<0.0003) and octanoyl (p<0.004) carnitines in patients with high-grade BLCA.