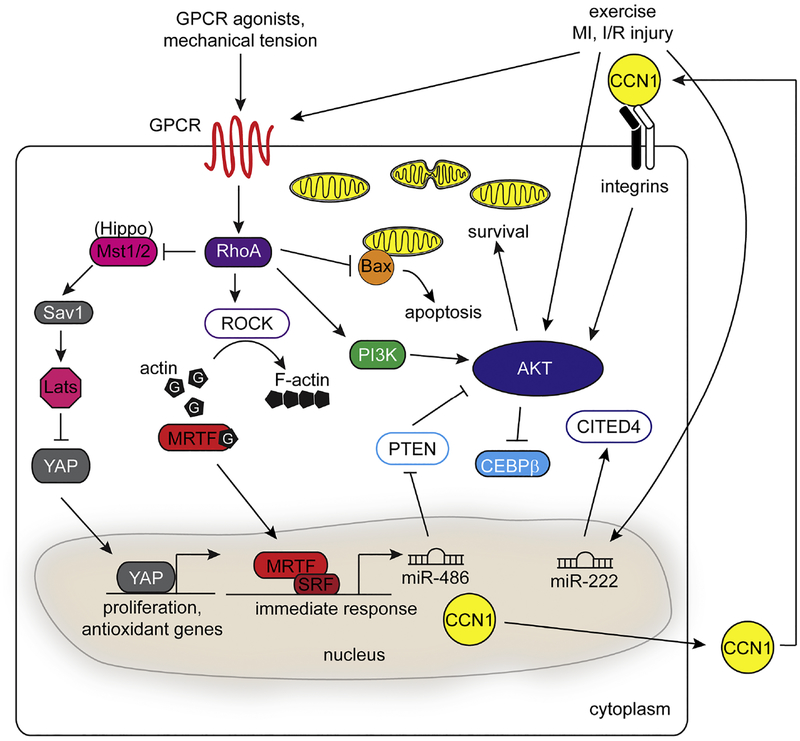
Figure 1.
Signaling pathways that modulate cardioprotection in CMs. Mechanical and oxidative stress produced in disease or exercise can induce a complex anti-apoptotic and hypertrophic response in CMs that converges on the RhoA and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Stimulation of GPCRs through ligands triggers RhoA-dependent actin polymerization and nuclear localization of MRTFs to activate transcription of MRTF/SRF target genes. Expression of targets such as miR-486 and CCNs, as well as exercise-induced mechanical tension can activate the Akt response to contribute to cardioprotection. RhoA can also modulate the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway to regulate proliferation and stress responsive genes during both development and disease.