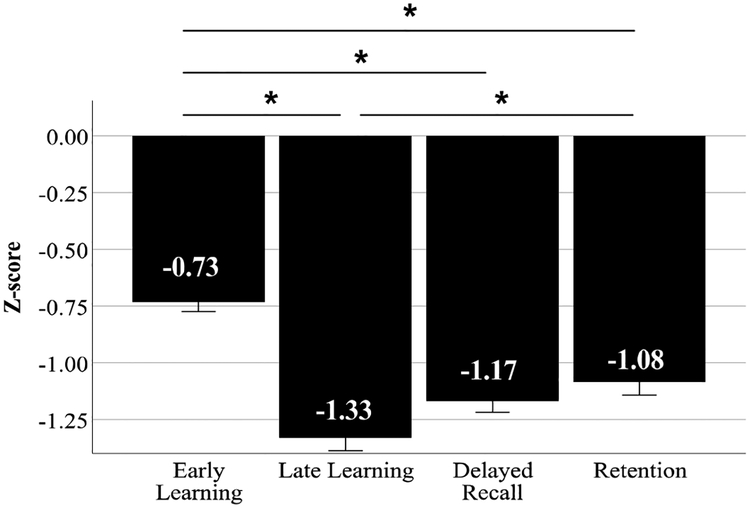
Figure 2. RAVLT performance in the entire aMCI+ group (n=338) revealed greatest impairment in Late Learning and Delayed Recall, compared to Early Learning or Retention.
Normed relative to the CN- group, aMCI+ performance on Late Learning (z-score = −1.33 ± 1.01) and Delayed Recall (z-score = −1.17 ± 0.90) were more impaired compared to Early Learning (z-score = −0.73 ± 0.77) and Retention (z-score = −1.08 ± 1.07). This aMCI+ group was inclusive of individuals who performed at floor levels on the delayed recall component of the RAVLT and who were more impaired on all other RAVLT trials as indicated in Supplementary Material Table 1. *indicates statistical significance at p <0.005. Error bars indicate ±1 standard error of the mean.