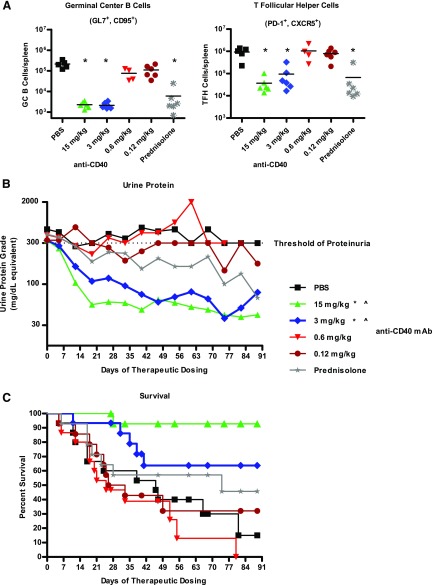
FIGURE 3.
Therapeutic treatment of female NZB/W-F1 mice with anti-CD40 mAb 201A3 reversed severe proteinuria and extends survival. Beginning at 26 wk of age, NZB/W-F1 mice were monitored for the development of proteinuria and enrolled into a therapeutic study when they reached ≥300 mg/dl of urine protein. (A) The numbers of GC B cells and Tfh cells per spleen, determined as described in Fig. 2, are shown (n = 4–6). *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA compared with PBS control. (B) Shown are the average urine protein levels of treated mice and (C) Kaplan–Meier graph showing percent survival following treatment with PBS, 201A3, or prednisolone (n = 14 or 15 per group). Note that because this study required a rolling enrollment the x-axis is days of dosing rather than age. Treatment duration was from 4 to 12 wk. The dotted line at 300 mg/dl is the threshold of proteinuria that triggered the initiation of treatment. p < 0.05 using repeated measures ANOVA and log-rank Mantel–Cox survival test, respectively. *, urine protein; ^, survival.