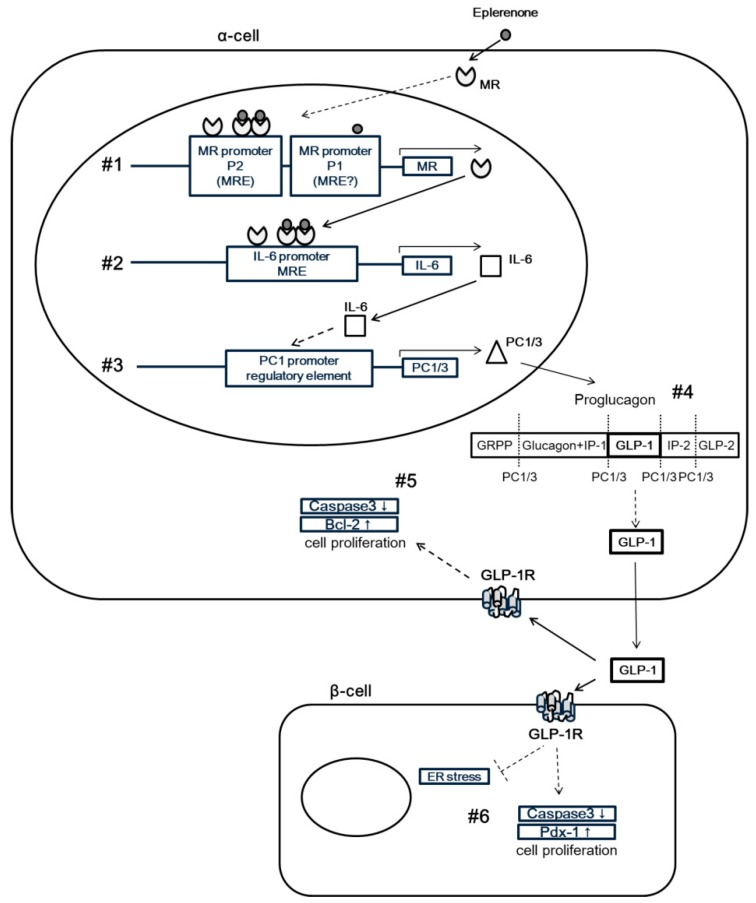
Figure 8.
Proposed mechanism for MR in pancreatic islets. MR signal exerts a protective function in islets through IL-6 induction, which promotes active GLP1 secretion through PC1/3 activation. (1) MR induced from eplerenone, alone or in an eplerenone-MR complex, may bind to MRE in P2 in α-cells and promote MR expression. (2) MR and/or an eplerenone-MR complex may bind to the MRE in the IL-6 promoter to drive IL-6 expression. (3) IL-6 activation leads to increased PC1/3 mRNA levels and (4) induced PC1/3 may cleave proglucagon into GLP-1 in α-cells, resulting in elevated plasma levels of GLP-1. (5) Autocrine signaling of GLP-1 in α-cells may increase the expression of Bcl-2 mRNA and reduce the levels of caspase-3 mRNA, leading to protection of α-cells from apoptosis. (6) Paracrine signaling of GLP-1 in β-cells may increase the expression of Pdx-1 mRNA and reduce the levels of caspase-3 mRNA, thus protecting β-cells from endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis.