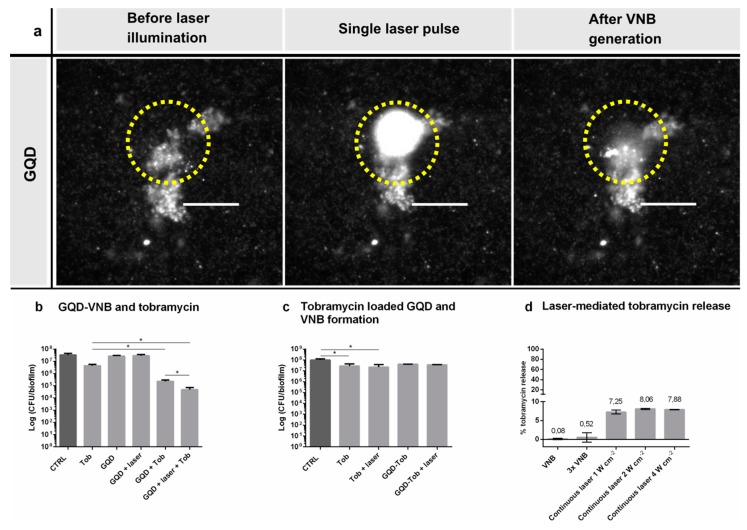
Figure 3.
Evaluation of combining tobramycin loaded GQD with laser-induced VNB for P. aeruginosa biofilm treatment. (a) VNB formation around GQD in P. aeruginosa biofilms. Dark field pictures were taken before, during and immediately after a single nanosecond laser pulse (561 nm, 7 ns). The yellow circle indicates the laser beam area. Scale bar = 100 µm. (b) The effect of GQD-induced VNB on tobramycin in the treatment of P. aeruginosa biofilms (average ± SD). CTRL: 0.9% NaCl (w/v), Tob: tobramycin at 16 µg mL−1, GQD: only addition of GQD, laser: pulsed laser treatment. (n = 3 × 3) (p-values < 0.05 were considered significant). (c) Anti-biofilm effect of laser-irradiated GQD loaded with tobramycin in P. aeruginosa biofilms (average ± SD). CTRL: 0.9% NaCl (w/v), Tob: tobramycin 16 µg mL−1, laser: pulsed laser treatment, GQD-Tob: GQD containing tobramycin at 16 µg mL−1 (n = 3 × 3) (p-values < 0.05 were considered significant). (d) Tobramycin release from GQD-tobramycin nanoparticles was quantified for different laser settings: single and repeated (3) VNB formation at a laser fluence of 2.00 J cm−2, and continuous laser illumination at 980 nm for 10 min at 1, 2 and 4 W cm−2 (mean ± SD).