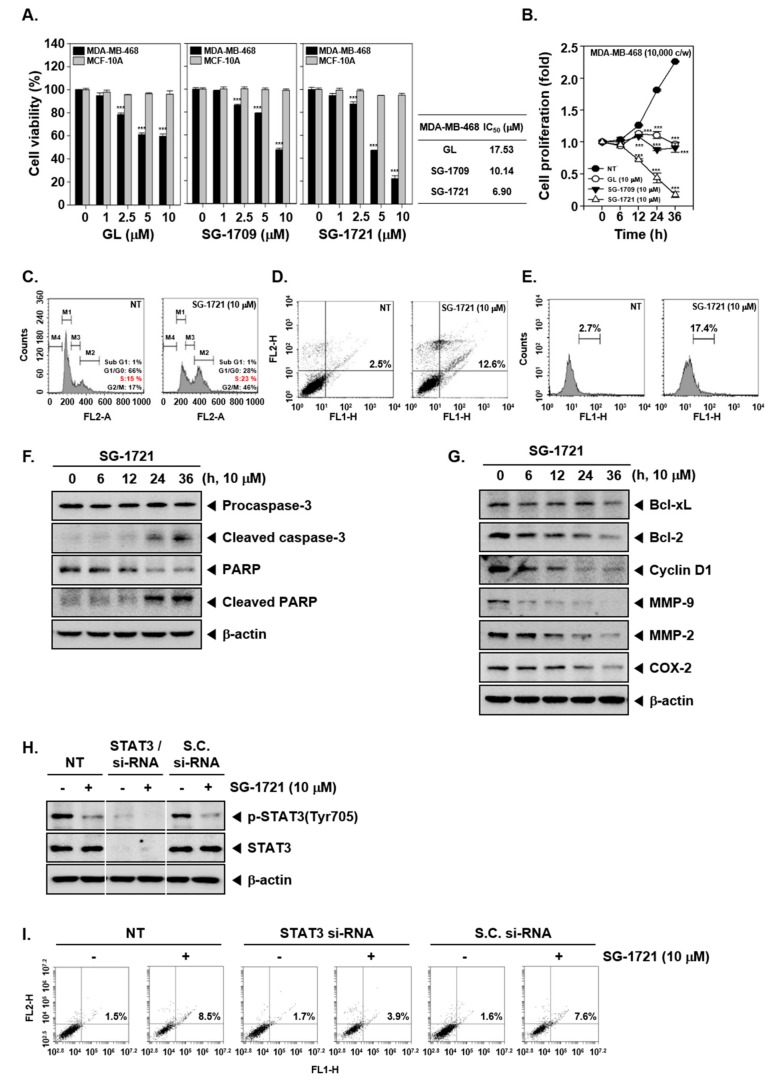
Figure 3.
GL and its analogues can cause apoptosis. (A) MDA–MB-468 and MCF-10A cells were treated with various concentrations of GL, SG-1709, and SG-1721 for 24 h, and cell viability was determined using the MTT (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay (left panel). IC50 values were determined as the drug concentration at 50% inhibition of the cell viability (right panel). *** p < 0.001. (B) MDA–MB-468 cells (10,000 cells/wells) were seeded for overnight and then treated with 10 μM of GL, SG-1709, and SG-1721, and cell proliferation assay was done. *** p < 0.001. (C) MDA–MB-468 cells were treated with 10 μM of SG-1721 for 24 h. Cellular DNA staining incorporating propidium iodide (PI) and flow cytometry analysis was carried out to determine the cell-cycle distribution. (D) MDA–MB-468 cells were treated as described in panel C, stained with FITC (fluorescein-5-isothiocyanate)-conjugated anti-Annexin V, and flow cytometer was used for analysis. (E) MDA–MB-468 cells were treated as described in panel C, and terminal transferase mediated dUTP-fluorescein nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining was performed (F–G) MDA–MB-468 cells were treated with 10 μM of GL, SG-1709, and SG-1721 for various intervals, and Western blot analysis was done. (H) MDA–MB-468 cells were transiently transfected with STAT3 or scrambled si-RNA (control). Then, the transfected cells were treated with 10 μM of SG-1721 for 4 h. Thereafter, Western blot analysis was carried out. (I) The transfected MDA–MB-468 cells were treated with 10 μM of SG-1721 for 24 h, and then annexin V assays was carried out as described above in panel D.