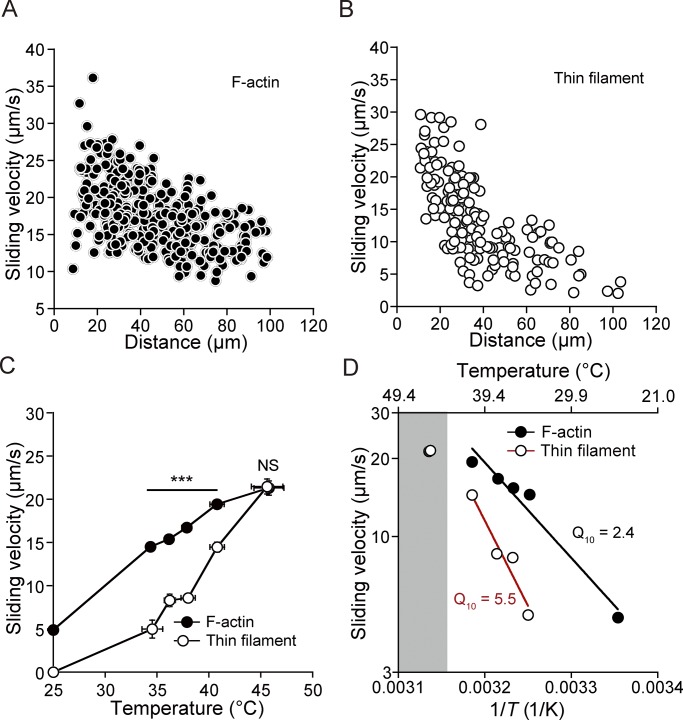
Figure 3.
Temperature dependence of sliding velocity of F-actin and reconstituted thin filaments at pCa 9. (A) Relationship between the distance from the heat source and sliding velocity for F-actin. (B) Same as in A for reconstituted thin filaments. (C) Sliding velocity plotted against temperature. Closed circles, F-actin; open circles, reconstituted thin filaments. Sliding velocities were compared at 25°C (baseline temperature) and at higher temperatures raised by IR laser irradiation. Data represent mean ± SEM for both the x and y axes. Sliding velocities at 25°C are 4.9 ± 0.1 µm/s (n = 513) and ∼0 µm/s for F-actin and reconstituted thin filaments, respectively. Those at higher temperatures are as follows: 14.5 ± 0.4 (n = 32) and 5.0 ± 1.0 µm/s (n = 6) at 34.4 ± 0.4 and 34.5 ± 1.0°C, 15.4 ± 0.4 (n = 65) and 8.3 ± 0.7 µm/s (n = 20) at 36.1 ± 0.4 and 36.2 ± 0.5°C, 16.7 ± 0.4 (n = 92) and 8.6 ± 0.5 µm/s (n = 26) at 37.9 ± 0.5 and 38.0 ± 0.7°C, 19.4 ± 0.4 (n = 120) and 14.5 ± 0.6 µm/s (n = 89) at 40.8 ± 0.7 and 40.8 ± 0.7°C, and 21.3 ± 0.8 µm/s (n = 39) and 21.5 ± 0.9 µm/s (n = 28) at 45.8 ± 1.4 and 45.6 ± 1.5°C for F-actin and reconstituted thin filaments, respectively. ***, P < 0.001 for the y axis between groups (no significant differences present on the x axis for each comparison). (D) Arrhenius plot of sliding velocity for F-actin and reconstituted thin filaments. T, absolute temperature. The average values from C were used. Data obtained in the highest temperature range (shown in gray) were not employed for the analysis due to possible denaturation of myosin (see Shriver and Kamath, 1990). Sliding velocity (V) and temperature were expressed in logarithm. F-actin: V = exp (30.06 − 8,468/T) (R = 0.96). Reconstituted thin filaments: V = exp (50.96 − 15,161/T) (R = 0.98). Closed circles with a black solid line, F-actin; open circles with a red solid line, reconstituted thin filaments. Q10, 2.4 (25–41°C) and 5.5 (34–41°C) for F-actin and reconstituted thin filaments, respectively.