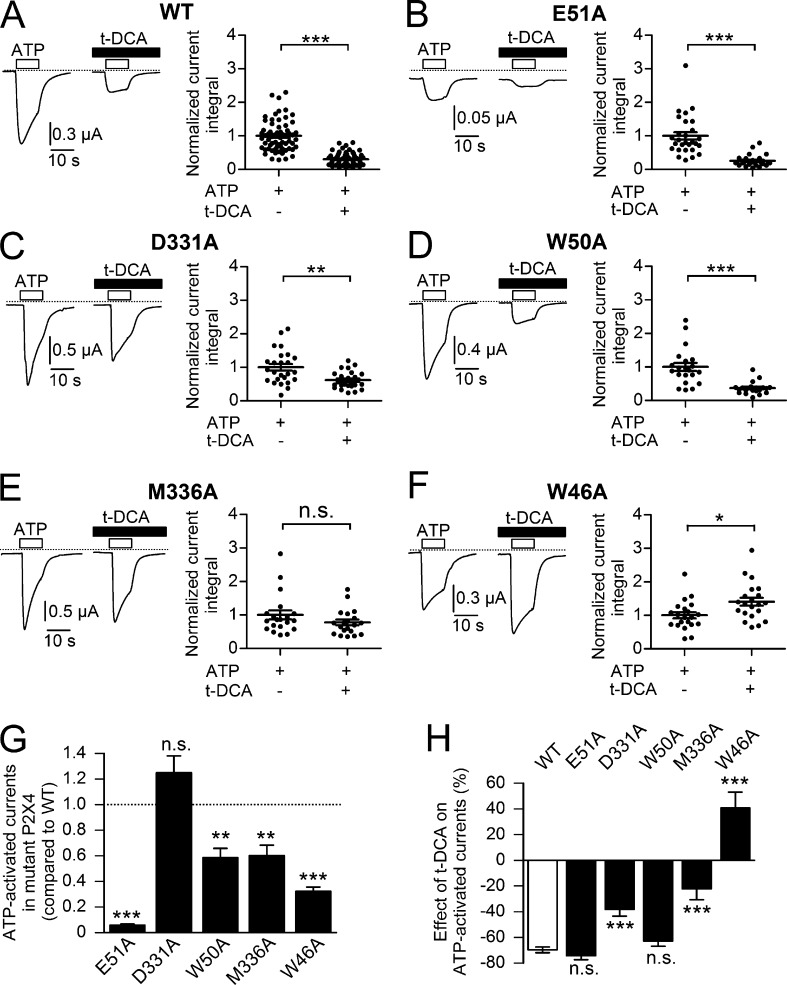
Figure 9.
D331, M336, and W46 are critically involved in t-DCA–mediated inhibition of P2X4. (A–F) Left panels: Representative whole-cell current traces recorded in oocytes expressing human WT (A) or mutant (B: E51A; C: D331A; D: W50A; E: M336A; F: W46A) P2X4. ATP (10 µM) and t-DCA (250 µM) were present in the bath solution as indicated by open and filled bars, respectively. Zero current level is indicated by a dotted horizontal line. Right panels: Summary of results from similar experiments as shown in the corresponding left panels. Current integrals were normalized as described in Fig. 2. Values are means ± SEM and individual data points are shown (A: n = 65; N = 7; B: n = 28; N = 3; C: n = 25; N = 3; D: n = 21; N = 2; E: n = 20; N = 2; F: n = 21; N = 2); ***, **, *, Significantly different, P < 0.001, P < 0.01, and P < 0.05, respectively; n.s., not significant; Student’s ratio t test. (G) Basal ATP-activated currents of mutant P2X4 channels compared with WT P2X4 from the same experiments as shown in A–F. The ATP-activated current integral was calculated in each recording and was normalized to the mean current integral determined in matched control oocytes (i.e., expressing WT P2X4) from the corresponding batch of oocytes (normalized to WT). Data are means ± SEM. ***, **, Significantly different compared with WT, P < 0.001 and P < 0.01, respectively; n.s., not significant; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. (H) Relative effects of t-DCA on ATP-activated P2X4 currents (negative values indicate inhibition; positive values indicate stimulation) in oocytes expressing WT P2X4 or different P2X4 mutant channels. The current integral calculated in each recording was normalized as described in Fig. 2. Data are means ± SEM of the normalized current integrals in the presence of t-DCA from the same experiments as shown in A–F. ***, Significantly different compared with WT, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test.