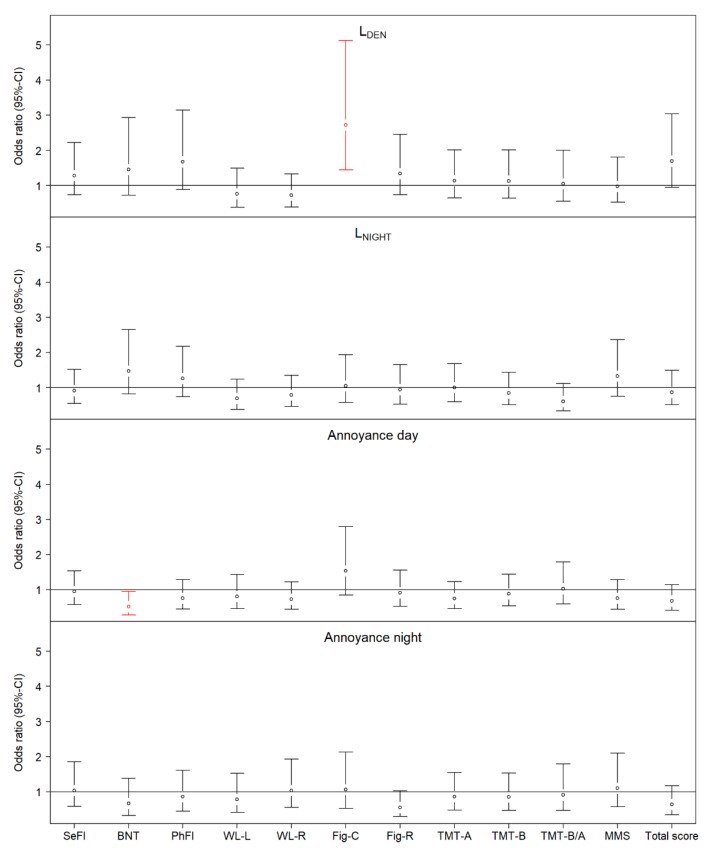
Figure 2.
Association of residential noise and noise annoyance with dichotomized cognitive scores. Adjusted for age (linear, squared, and cubic terms), smoking, passive smoking, and educational level. We modeled the probability that score < 0 (cognitive performance lower than expected for the participant’s age and educational level). Statistically significant associations (p < 0.05) are marked red.