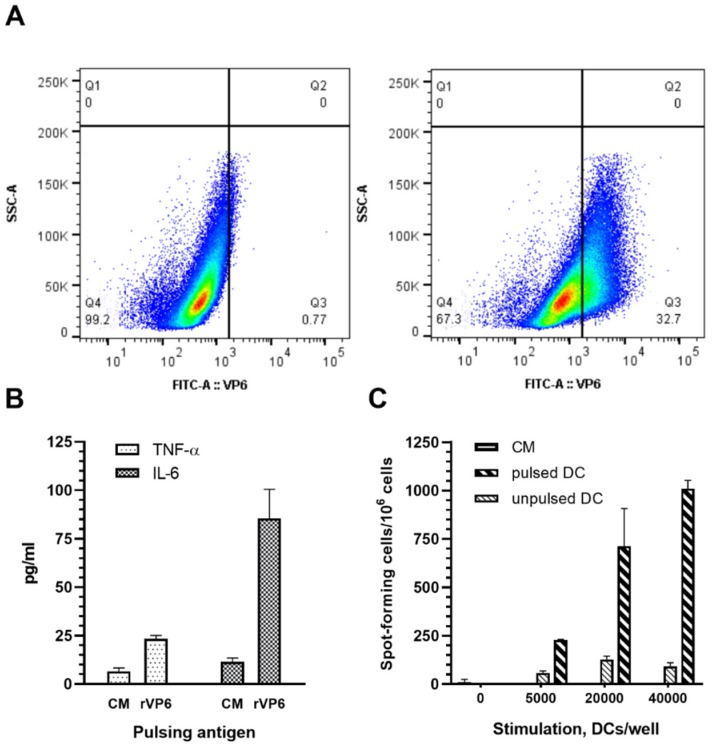
Figure 7.
Rotavirus (RV) VP6 internalization, activation and presentation by bone-marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs). Mouse BMDCs incubated for 20 h in the presence of (A, left panel) 100 µg/mL RV VP6 were intracellularly stained for RV VP6 and uptake of VP6 was analyzed by flow cytometry. BMDCs incubated in (A, right panel) culture media (CM) only served as negative controls. Uptake of VP6 is shown in the SSC-A versus VP6-FITC density dot plot on BMDCs gated on viable cells, a representative of repeated experiments. (B) TNF-α and IL-6 cytokines secretion by BMDC in response to VP6 was measured from CM collected at the end of the incubation period using ELISA. Shown are mean values (pg/mL) of the repeated analysis with standard errors of the mean. (C) VP6-pulsed BMDC were used at three different concentrations to stimulate VP6-specific mouse splenocytes in ELISPOT IFN-γ assay. Results are expressed as the mean spot forming cells (SFC) per 106 splenocytes of the duplicate wells with standard errors of the mean.