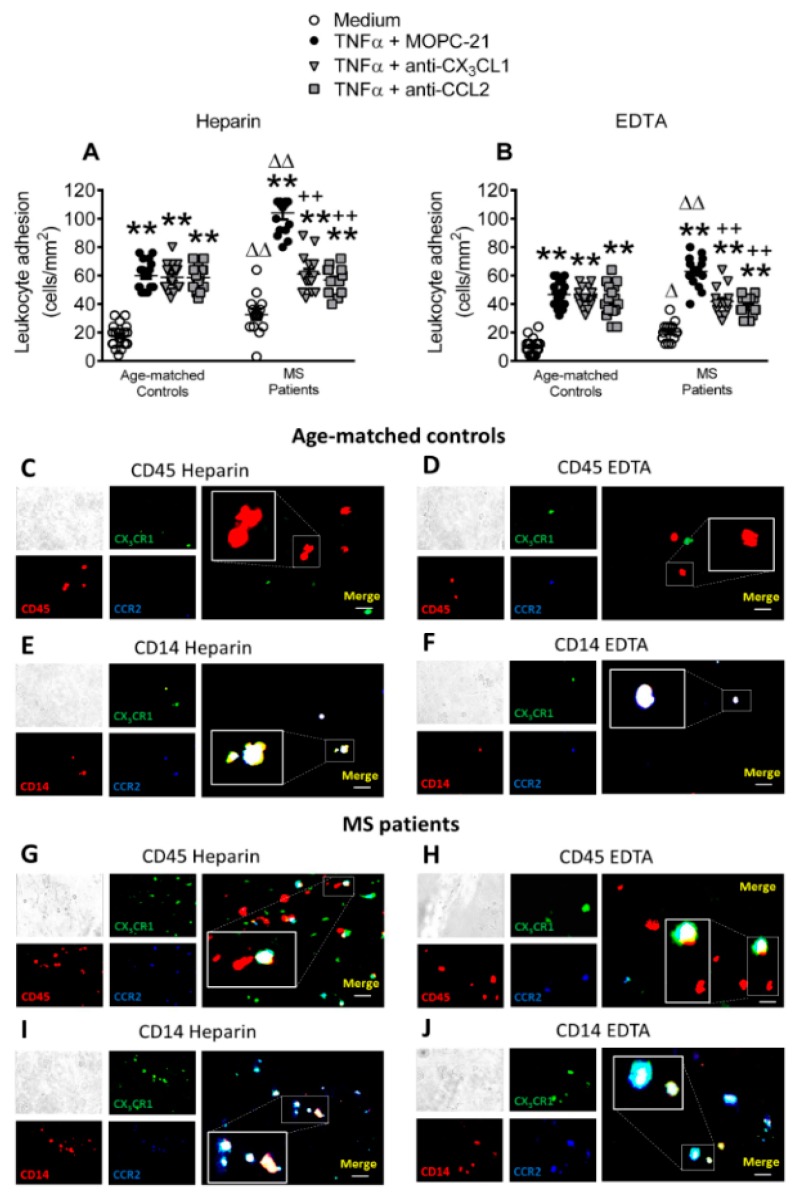
Figure 7.
Circulating leukocytes from metabolic syndrome patients show increased adhesiveness to TNFα-stimulated HUAECs, which is partly dependent on both CX3CL1/CX3CR1 and CCL2/CCR2 interactions. HUAEC were stimulated with TNFα (20 ng/mL) for 24 h. Some of the cells were incubated with a CX3CL1 or a CCL2 neutralizing antibody or an isotype-matched control antibody (MOPC-21). Subsequently, whole blood from metabolic syndrome patients and age-matched controls incubated without (A) or with (B) EDTA was perfused across endothelial monolayers for 7 min at 0.5 dyn/cm2 and leukocyte adhesion quantified (n = 21 control subjects and n = 18 metabolic syndrome patients). Results are presented as leukocyte adhered per mm2 (cells/mm2). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. ** p < 0.01 relative to values in medium; ++p < 0.01 relative to TNFα+MOPC-21; ∆p < 0.05 or ∆∆p < 0.01 relative to the respective age-matched control group. Immunofluorescence analysis showing adherent platelet–leukocyte cell complexes, platelet-monocyte aggregates, leukocytes or monocytes to TNFα-stimulated HUAEC (C–J). Heparinized blood from age-matched controls and patients with metabolic syndrome was incubated without or with EDTA. After the flow chamber assay, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and blocked in PBS containing 1% BSA. Subsequently, cells were incubated for 2 h with an Alexa 594-conjugated antibody against human CD45 to detect leukocytes (1:50 dilution, red, C,D,G,H) or an APC-conjugated antibody against human CD14, to detect monocytes (1:50 dilution, red, E,F,I,J). Additionally, all of the cells (C–J) were incubated for 2 h with an Alexa Fluor 350-conjugated antibody against human CCR2 (1:50 dilution, blue) and a FITC-conjugated antibody against human CX3CR1 (1:50 dilution, green). Images were captured with a Zeiss Axio Observer A1 fluorescence microscope. Bar graph = 50 μm.