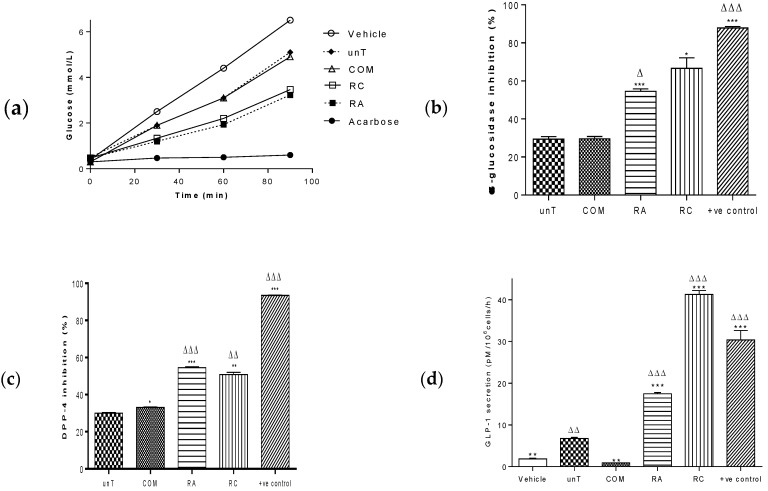
Figure 1.
Bioactivity of rol gene transformed L. sativa. α-glucosidase inhibition by L. sativa. (a) Liberation of glucose from maltose over time and (b) percentage α-glucosidase inhibitory for each L. sativa extract (0.25–1.0 mg/mL; n = 3). Positive control was acarbose (1 mg/mL) (c) DPP-4 inhibition for each L. sativa extract (0.25–1.0 mg/mL; n = 3). Positive control was berberine (1 mg/mL) (d) GLP-1 secretory responses of each L. sativa extract (1.0 mg/mL; n = 4). Positive control was α-lactalbumin (10 mg/mL). All values are mean ± SEM. All statistical comparisons were One Way ANOVA. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 compared with UnT ∆ p < 0.05, ∆∆ p < 0.01 and ∆∆∆ p < 0.001 compared with COM. unT = untransformed cultured; COM = commercially obtained; RA = rol ABC transformed and RC = rol C transformed. Inhibitory activities (α-glucosidase and DPP-4) were calculated as a percentage of the vehicle control.