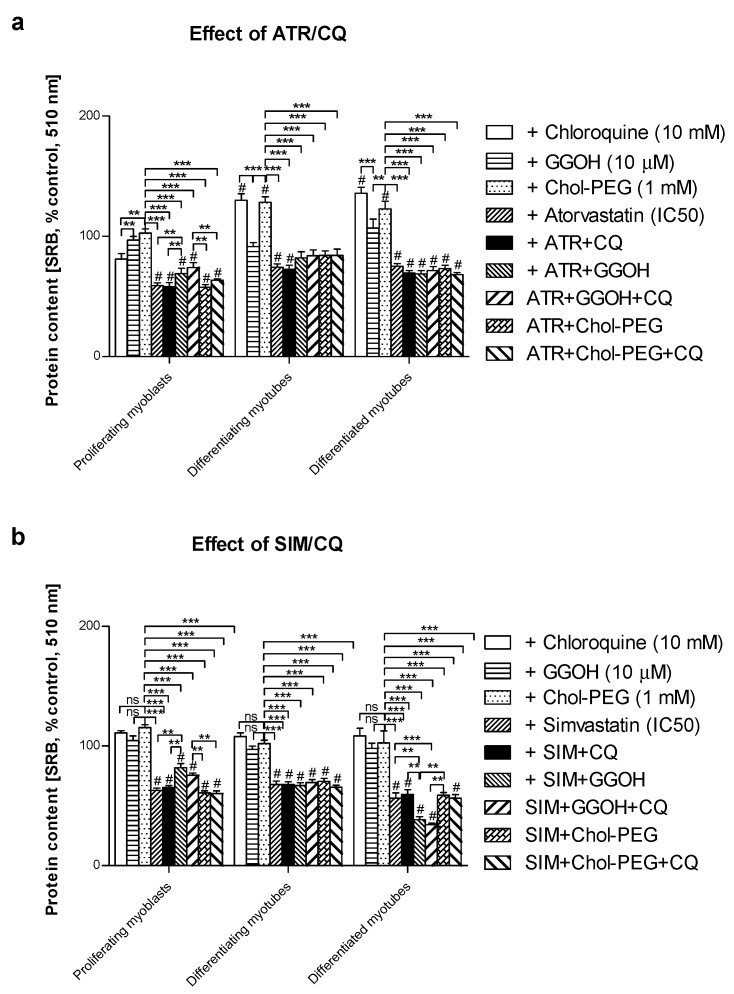
Figure 2.
Effect of geranylgeraniol (GGOH, µ10 M) on the protein content (sulforhodamine B (SRB) incorporation) affected by MEV pathway modulators (atorvastatin—ATR, simvastatin—SIM) or water-soluble cholesterol (Chol-PEG) in the presence or absence of chloroquine (CQ, 10 mM). Differentiating C2C12 myoblasts were exposed for 24, 72 or 120 h to statins (IC50) or water-soluble cholesterol (Chol-PEG), (Day 1—proliferating myoblasts; Day 3—differentiating myotubes; Day 5—differentiated myotubes). (a) ATR diminished the protein content in viable cells (IC50). Neither CQ nor Chol-PEG or GGOH affected the protein content in comparison to control untreated cells (p > 0.05); GGOH but not Chol-PEG recovered cellular protein content reduced by ATR in proliferating myoblasts (p < 0.001). The effect of GGOH was not affected by CQ administration (p > 0.05); (b) SIM diminished the protein content in viable cells (IC50). Neither CQ nor Chol-PEG or GGOH affected the protein content in comparison to control untreated cells (p > 0.05); GGOH but not Chol-PEG recovered the cellular protein content reduced by SIM in proliferating myoblasts (p < 0.001). GGOH worsened the protein content that had been diminished by SIM in differentiated myotubes (p < 0.01). The effect of GGOH was not affected by CQ administration (p > 0.05); *** p < 0.001, for comparison between the means. Statistically significant differences from untreated control cells are marked by # (at least at the level of p < 0.05, ns—non significant). The results are indicative of three independent experiments performed in eight replicates.