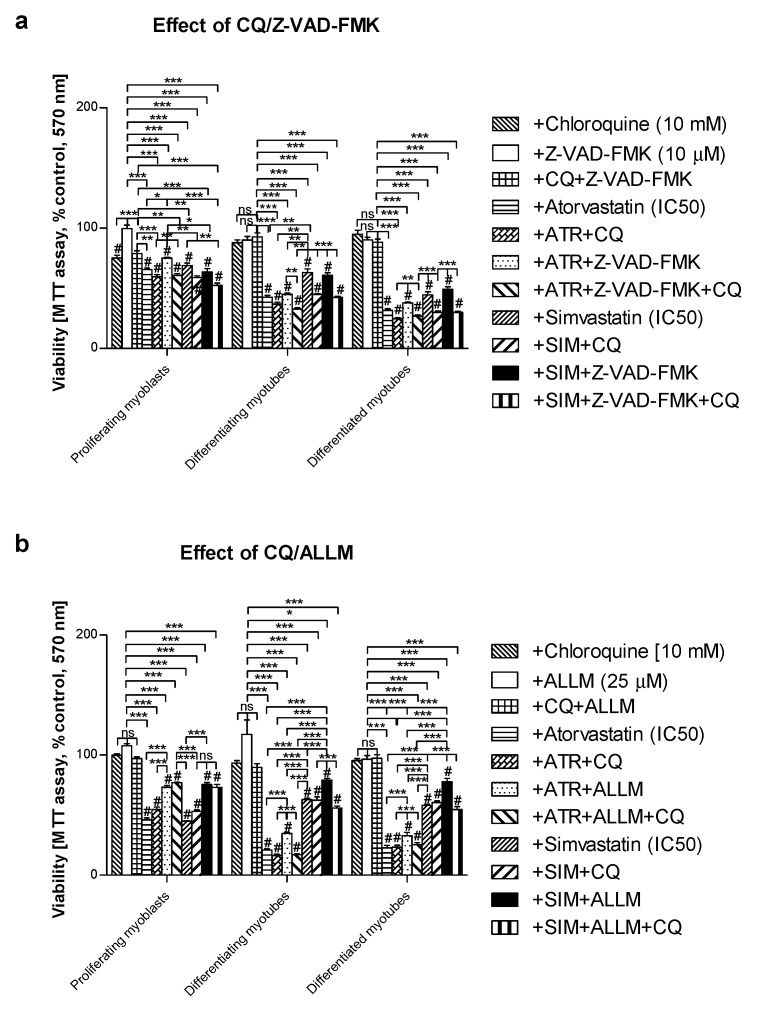
Figure 6.
Effect of pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK or calpain inhibitor ALLM on cell viability (MTT assay) affected by MEV pathway modulators (atorvastatin—ATR, simvastatin—SIM) in the presence or absence of chloroquine (CQ, 10 mM). Differentiating C2C12 myoblasts were exposed for 24, 72, or 120 h to statins (IC50), (Day 1—proliferating myoblasts; Day 3—differentiating myotubes; Day 5—differentiated myotubes). (a) Both ATR and SIM diminished cell viability (IC50). Z-VAD-FMK itself had no effect on cell viability (p > 0.05). However, it overruled the myotoxicity evoked by ATR but not SIM administration in proliferating myoblasts only (p < 0.05). Upon CQ addition, the cell viability that had already been reduced by ATR or SIM co-treatment shrunk considerably further (p < 0.01). (b) ALLM itself had no effect on cell viability (p > 0.05). In contrast to Z-VAD-FMK, ALLM (25 μM) markedly recovered cells from ATR- or SIM-dependent myotoxicity in proliferating myoblasts, differentiating and differentiated myotubes (p < 0.001). ALLM recovered muscle cell viability less efficiently in ATR- than in SIM-dependent SAM. Statistically significant differences from untreated control cells are marked by # (at least at the level of p < 0.05, ns—non significant). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. The results are indicative of three independent experiments performed in eight replicates.