Fig. 3.
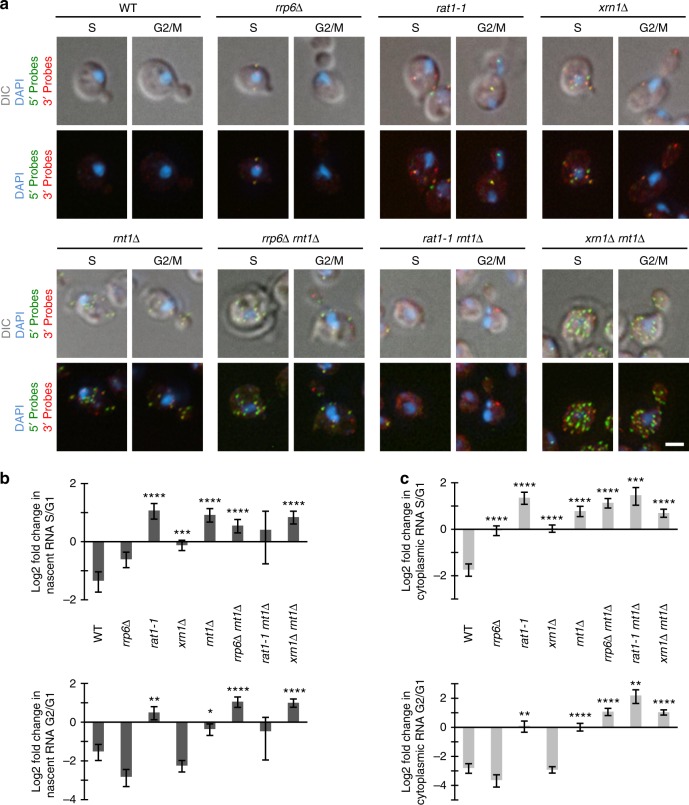
Nuclear ribonucleases are essential for the cell cycle-dependent repression of AXL2. a smFISH analysis of cells with the various ribonuclease mutations shown. The expression of Axl2 mRNA was monitored in wild type cells (WT) or cells with single (rrp6∆, rat1-1, rnt1∆, and xrn1∆) or double (rrp6∆ rnt1∆, rat1-1 rnt1∆, xrn1∆, and xrn1∆ rnt1∆) mutations in different nuclear or nuclear/cytoplasmic ribonucleases. FISH analysis was performed as described in Fig. 1 and examples of cells in the S and G2/M phases, when AXL2 is normally repressed, are shown. The white bar equals 2 µm. b Quantification of ribonuclease-dependent changes in nascent RNA levels (5′ end probe) in S (top panel) or G2/M (bottom panel). Nascent RNA detected in the nucleus was quantified in different phases and the Log2 change between S or G2/M relative to G1 is plotted for each mutant strain. c Effect of ribonuclease mutations on the abundance of cytoplasmic Axl2 mRNA. The total amount of full-length RNA detected in different phases was quantified and the Log2 change between the S (top panel) or G2/M (bottom panel) relative to G1 is plotted for each mutant strain. All error bars represent the uncertainties calculated from the standard errors of the mean (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 by two-tailed unpaired t test with Welch’s correction)