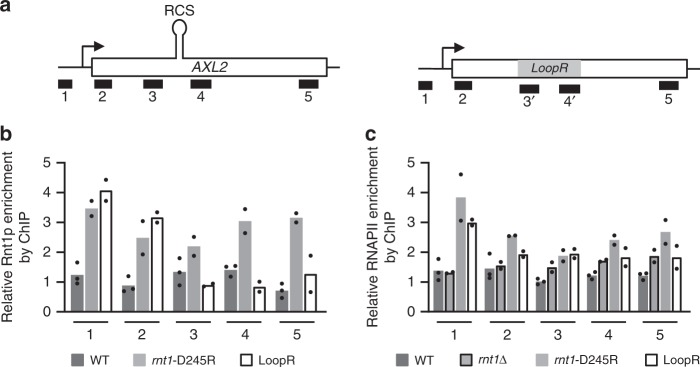
Fig. 6.
Rnt1p associates with both the promoter and RNA of AXL2. a Schematic representation of the AXL2 locus depicting the position of the different fragments amplified by qPCR after chromatin immunoprecipitation. The position in the RNA of the Rnt1p cleavage site (RCS) is shown on top. The position of the loop sequence replacement is shown by a gray box. 3′ and 4′ indicate probe sets specific to the mutated sequence (LoopR). b Rnt1p associates with AXL2 chromatin in both a promoter and RNA-cleavage site-dependent manner. Chromatin was immunoprecipitated using wild type cells (WT), cells expressing a catalytically impaired version of Rnt1p (rnt1-D245R) or cells expressing Axl2 mRNA lacking the sequence of the cleavage site (LoopR). The chromatin was precipitated using antibodies against Rnt1p46 and different fragments of AXL2 were amplified using qPCR analysis using AXL2 specific probes. The position of the different amplicons is illustrated in (a). c The deletion of RNT1 increases RNAPII association with the AXL2 locus. Chromatin was immunoprecipitated from the different cells described in (b) and rnt1∆ with antibodies against RNAPII and the enrichment of the different AXL2 fragments was evaluated using qPCR as described in (b). The enrichments were measured relative to a non-coding region of chrV. The bar graphs represent an average of 3 biological replicates for the wild type strains and 2 biological replicates for all other strains. The data points are shown in the form of dots