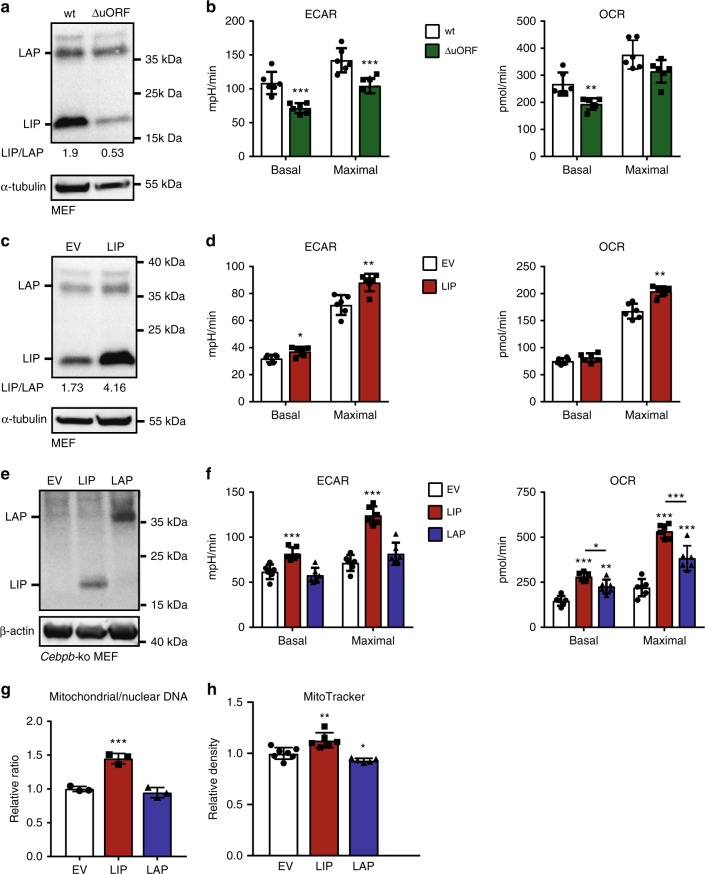
Fig. 1.
C/EBPβ-LAP and -LIP isoforms regulate cellular metabolism. a Immunoblot analysis of C/EBPβ-LAP and C/EBPβ-LIP expression in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) derived from wt or C/EBPβΔuORF mice. α-tubulin is used for loading control. Uncropped images are shown in Supplementary Fig. 7. b Extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) and oxygen consumption rate (OCR) of MEFs derived from wt or C/EBPβΔuORF mice (n = 6). c Immunoblot analysis of C/EBPβ-LAP and C/EBPβ-LIP expression in wt MEFs and with ectopic expression of LIP. α-tubulin is used for loading control. Uncropped images are shown in Supplementary Fig. 7. d ECAR and OCR of wt MEFs with control empty vector (EV) or ectopic expression of LIP (n = 6). e Immunoblot analysis of C/EBPβ-LAP and C/EBPβ-LIP expression in Cebpb-knockout (ko) MEFs with control empty vector (EV) or ectopic expression of LIP or LAP. β-actin is used for loading control. Uncropped images are shown in Supplementary Fig. 7. f ECAR and OCR of Cebpb-ko MEFs with control empty vector (EV) or ectopic expression of LIP or LAP (n = 6). g Mitochondrial/nuclear DNA ratio and h MitoTracker quantification of Cebpb-ko MEFs with control empty vector (EV) or ectopic expression of LIP or LAP (n = 7 for EV, n = 6 for LIP and n = 5 for LAP). Statistical differences were analysed by Student’s t-tests. Error bars represent SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0. 001