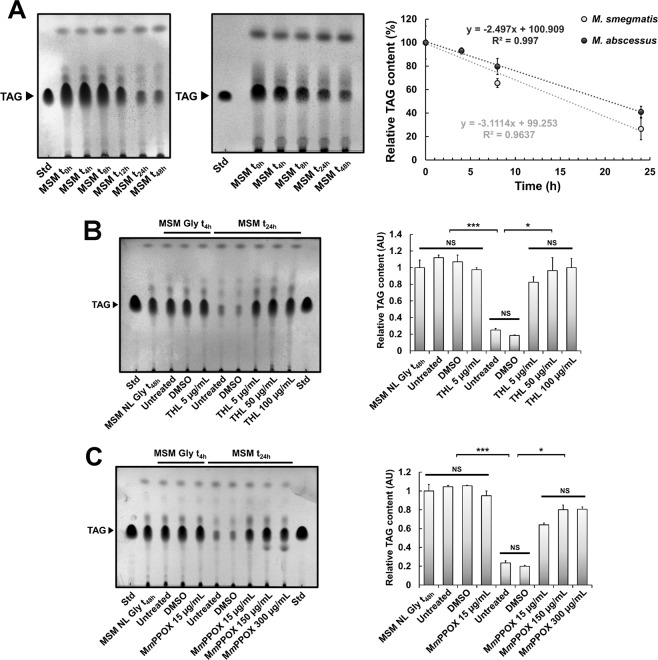
Figure 3.
ILI hydrolysis is a reversible and rapid phenomenon upon carbon starvation and is mediated by lipolytic enzymes. (A) ILI hydrolysis occurs rapidly during carbon starvation. Lipid rich mycobacterial cultures were transferred into a carbon starved-MSM medium and collected at indicated time points, lyophilized and equal amounts of dry cells used for apolar lipid extraction. TAG levels from M. smegmatis (left panel) and M. abscessus (right panel) were analysed by TLC with triolein as standard. Each TLC plate is representative of individual experiments performed in triplicate. Variation of relative TAG content, assessed by densitometric analysis of the TLC plates obtained from M. smegmatis and M. abscessus cultures, as a function of time. Results are expressed as mean values ± SD of two independent experiments. (B-C) TAG hydrolysis and ILI consumption can be pharmacologically blocked by serine-hydrolase inhibitors. Lipid rich mycobacterial cultures were harvested, re-suspended in MSM Gly, pre-incubated with or without THL (B) or MmPPOX (C) for 4 h, centrifuged and finally incubated in MSM medium devoid of carbon for 24 h with the indicated concentration of THL (stock solution 5 mg/mL in DMSO) or MmPPOX (stock solution at 5 mg/mL in DMSO). Cells were collected at specific time points and their lipids were extracted and analysed by TLC analysis. Each TLC plate is representative of two independent experiments. TAG levels from each M. smegmatis culture were analysed by TLC with triolein as standard. Results from densitometry are expressed as mean values ± SD of two independent experiments. TAG band intensities of lipid rich, lipid poor (devoid of inhibitors) and lipid-rich inhibited cells (THL or MmPPOX) were compared using a one-way ANOVA test where * corresponds to a p-value < 0.05 and *** to a p-value < 0.001.