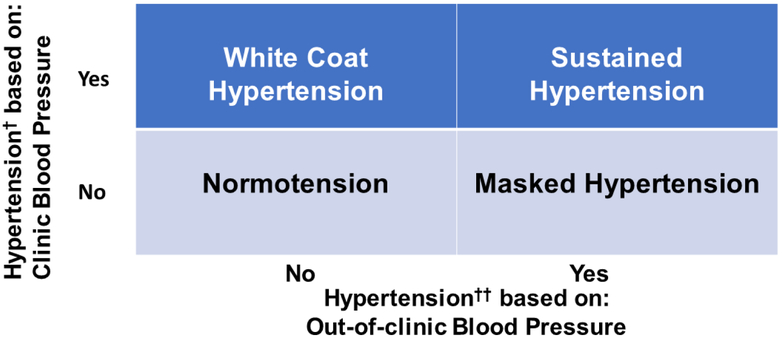
† ≥130/80 mm Hg is the threshold for clinic blood pressure recommended in the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guideline (≥140/90 mmHg was the threshold for clinic blood pressure used in Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure [JNC 7]). †† ≥130/80 mm Hg is the threshold for awake and home blood pressure recommended in the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guideline (≥135/85 mmHg was the threshold for awake blood pressure used in JNC7). Some guidelines also recommend considering 24-hour and asleep blood pressure. The terms listed in the figure refer to untreated individuals. Among individuals taking antihypertensive medication, the corresponding terms are:
White coat hypertension - white coat effect,
Masked hypertension - masked uncontrolled hypertension,
Sustained hypertension - uncontrolled hypertension
Normotension - controlled hypertension