Figure 1. Thorase variants have defects in Thorase oligomer and GluA2-GRIP1 complex disassembly.
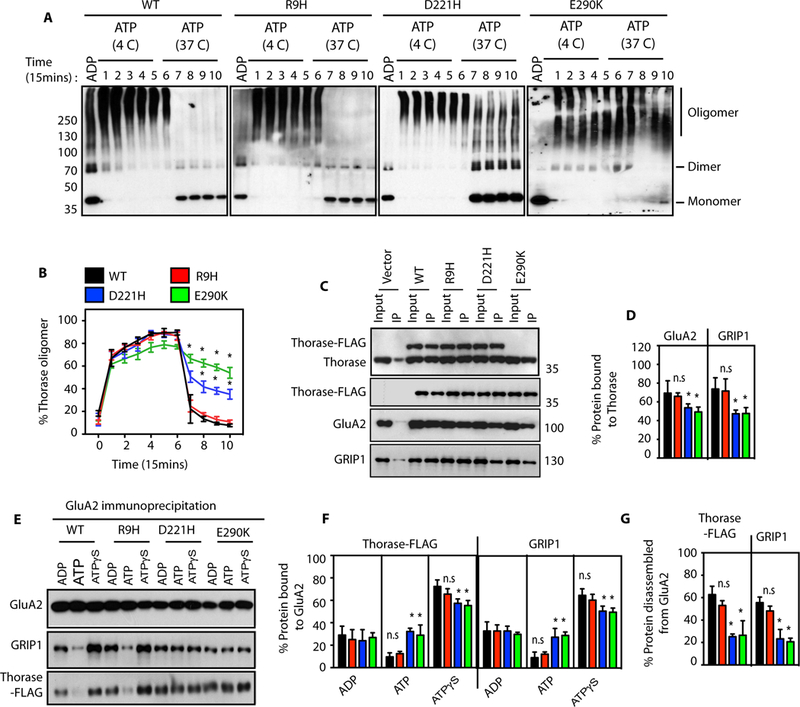
(A) Immunoblot analyses of Thorase wild type (WT) and variants oligomer formation. The samples were cross-linked by glutaraldehyde in the presence of 1 mM ADP or 1 mM ATP. The ATP treated samples were incubated at 4 °C (4 C) for Thorase oligomer formation and then at 37 °C (37 C) for ATP hydrolysis to disassembly Thorase oligomer. Samples were collected every 15 min over 150 min (lanes 1–10) during the incubation for cross-linking. (B) Graphical representation of the percentages of the oligomer states of Thorase at different times. (C) Immunoblot analyses of FLAG tagged Thorase immunoprecipitation (IP) from Thorase-heterozygous cortical neurons expressing FLAG tagged Thorase WT or variants in the presence of different nucleotides. The samples were resolved on 10% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-Thorase, anti-FLAG-HRP, anti-GluA2 and anti-GRIP1 antibodies. (D) Normalized percent bound GluA2 and GRIP1 in the Thorase-FLAG IP samples for (C). (E) Immunoblot analyses of GluA2 IP from Thorase-heterozygous cortical neurons expressing FLAG tagged Thorase WT or variants in the presence of different nucleotides. The samples were separated on 10% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-Flag, anti-GluA2 and anti-GRIP1 antibodies. (F) Normalized percent bound Thorase and GRIP1 in the GluA2 IP samples for (E). (G) The percent of Thorase and GRIP1 disassembled from the GluA2 complex upon ATP hydrolysis in (E). (mean ± standard error of the mean [SEM], n = 3, **p < 0.05, *p < 0.10, n.s. p > 0.10, Holm-Sidak post-hoc test compared with WT, Power: 1-β err prob = 0.8–1.0).
