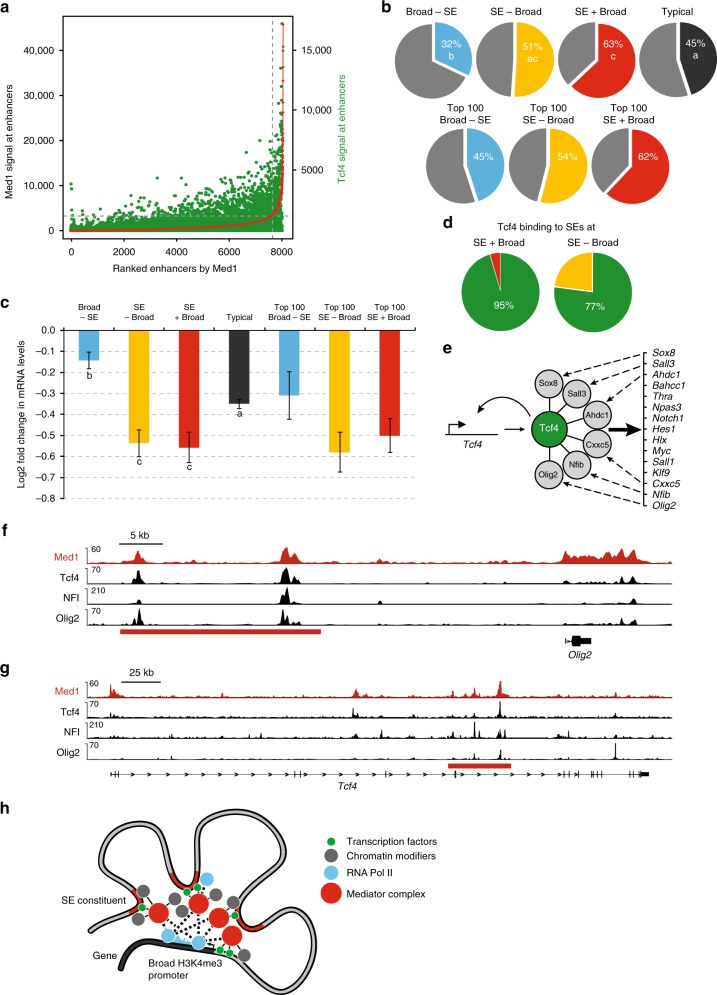
Fig. 7.
Tcf4 regulates neurogenic transcription factor genes with super enhancers and broad H3K4me3 promoters. a Tcf4 signal at enhancers ranked by Med1 content. Tcf4 ChIP-seq read content is in green, enhancers ranked by Med1 ChIP-seq read content is in red. b Percentages of downregulated genes in the different categories upon Tcf4 knock-down in NSCs. Percentages of down-regulated genes in all genes and top 100 genes within each category are shown. Statistically significant differences between groups are indicated as separate letters in the pie charts, p < 0.001 as assessed by Student t-tests. c Changes in mRNA levels of the different categories of genes upon Tcf4 knock-down in NSCs. Log2 fold change, based on RNA-seq data, is shown. Error bars indicate S.e.m., based on the RNA-seq triplicates. Statistically significant differences between groups are indicated as separate letters below the box plots, p < 0.001 as assessed by Student t-tests. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. d Percentage of Tcf4-bound SEs in SE + Broad genes or SE-Broad genes in NSCs. SEs nearest to SE + Broad genes or SE-Broad genes with or without significant Tcf4 binding sites, as determined by ChIP-seq, were counted. e Model of Tcf4-driven feed-forward transcriptional circuit of SE + Broad TF genes in NSCs. Fifteen15 SE + Broad TF genes bound at their SE and activated by Tcf4 are indicated. Tcf4 also binds its own SE. TF proteins encoded by six target genes also interact with Tcf4 protein and may aid in transcriptional regulation by Tcf4. f, g Overlap of binding sites of Tcf4 and Med1 with Tcf4-interactors Olig2 and NFI at the Olig2 gene (f) or Tcf4 gene (g) in NSCs. ChIP-seq tracks for the indicated proteins are shown. SE is indicated with a red bar. Range of reads per million per base pair is indicated on the y-axis. Scale bar is indicated. h Model of SE-Broad H3K4me3 promoter assemblies. TFs at SE constituents and the Broad H3K4me3 promoter recruit high levels of Mediator complex into SE-Broad assemblies. In turn, Mediator recruits high levels of protein–protein interaction partners such as the RNApol2 complex, Integrator, and chromatin modifiers. This would result in efficient pause-release of RNApol2 and high but TF-regulated levels of transcription