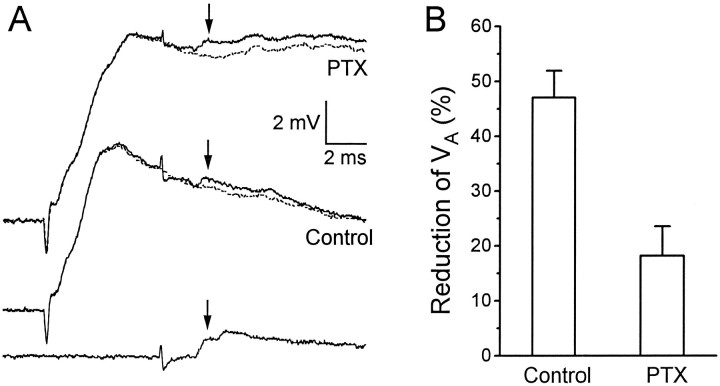
Fig. 5.
Effect of PTX on the reduction ofVA by the root-evoked PSP. A, Thebottom trace shows VA evoked in the absence of root stimulation. (The second “hump” in the trace, which was not considered for measurement, was a slightly later unitary EPSP associated with the firing of another interneuron.) Themiddle two traces are VA evoked during a root-evoked PSP (solid trace), superimposed on a root-evoked PSP alone (dashed trace); both middle traces were obtained in the absence of PTX. The top two traces are the same as the middle two tracesexcept that they were obtained in the presence of 7 μmPTX. All traces were recorded from the same animal. Thearrows point to the peak of VA in each case. B, Mean percentage reduction ofVA ± SEM when its peak was timed to occur 8.0 msec after the root stimulus, as in the example shown inA, in the absence (control; n = 10 animals) and presence of PTX (n = 3).