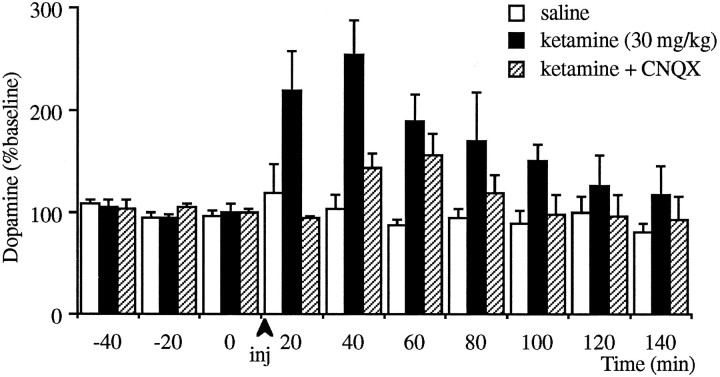
Fig. 3.
Effect of intraperitoneal injections of 30 mg/kg ketamine on the extracellular levels of dopamine in the prefrontal cortex in the presence or absence of local infusion of CNQX. Ketamine increased dopamine release significantly compared with saline-injected groups as determined by two-way repeated- measures ANOVA (p < 0.001, n = 9 for ketamine-treated group; n = 5 for saline-treated group). Infusion of CNQX (50 μm) started 1 hr before ketamine injection (n = 6). After this treatment, injection of ketamine only produced a trend toward an increase (p = 0.07). Furthermore, the effect of ketamine in CNQX-treated animals was significantly lower than CNQX-untreated animals (p < 0.05).