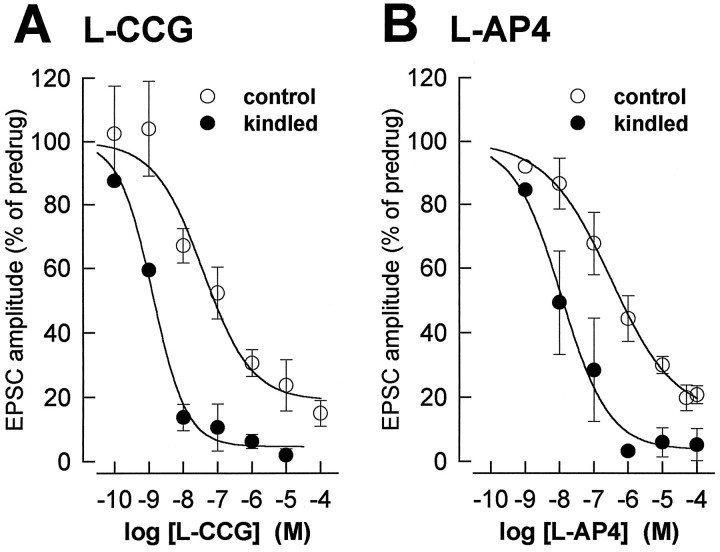
Fig. 3.
The concentration-dependent depression of synaptic transmission by mGluR agonists is enhanced in kindled neurons.A, The peak amplitudes of the EPSCs obtained with each concentration of l-CCG in control neurons (n = 22) and kindled neurons (n= 5) were averaged and expressed as percentage of predrug control values (100%). The two-way ANOVA revealed significant differences between control and kindled neurons (p < 0.0001) and between the different concentrations (p < 0.0001) but no significant interaction (p > 0.5), indicating a parallel shift. The EC50 (see Materials and Methods) is 30 × lower in kindled (1.2 nm) than in control neurons (36 nm). B, l-AP4 was less potent than l-CCG in depressing synaptic transmission. Effects ofl-AP4 on EPSC amplitudes in control (n= 27) and kindled neurons (n = 6) are displayed as in A. The two-way ANOVA detected significant differences between control and kindled neurons (p < 0.0001) and between the different concentrations (p < 0.0001) but no significant interaction (p > 0.5), thus indicating a parallel shift. The EC50 is 28 × lower in kindled (10.8 nm) than in control neurons (297 nm). Symbols and error bars represent mean ± SEM.