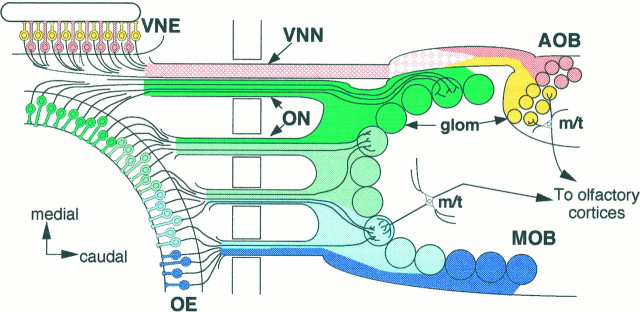
Fig. 1.
Zonal organization of the main and accessory olfactory systems. Schematic dorsal view of the olfactory systems. Olfactory sensory neurons in the four zones (zone I, dark green; zone II, light green; zone III,light blue; zone IV, dark blue) of the olfactory epithelium (OE) project their axons to four corresponding zones of the main olfactory bulb (MOB). Similarly, vomeronasal sensory neurons in the two zones (apical,yellow; basal, pink) of the vomeronasal epithelium (VNE) project their axons to two zones (rostral, yellow; caudal, pink) of the accessory olfactory bulb (AOB). Note that olfactory axons from different zones already are segregated spatially at the exit points of the OE, whereas the vomeronasal axons from the different zones are intermingled in the vicinity of theVNE and become segregated gradually near theAOB. ON, Olfactory nerves;VNN, vomeronasal nerves; glom, glomeruli;m/t, mitral and tufted cells.