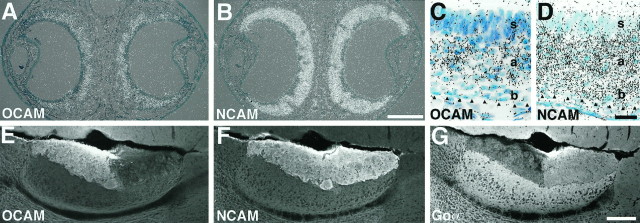
Fig. 6.
Zone-specific expression of OCAM in the accessory olfactory system. In situ hybridization analysis of coronal sections of the VNE from a P14 mouse (A–D) and immunohistochemical analysis of parasagittal sections of adult AOB (E–G).A, B, Superimposed images of bright-field and dark-field micrographs showing expression of OCAM (A) and NCAM (B) mRNAs in the crescent-shaped VNE. Dorsal is at the top. C, D, High-power bright-field micrographs of the center region of the VNE. The lumen is located at the top. The basal lamina is shown byarrowheads. Note that OCAM is expressed in the apical zone (a) of the VNE, but not in the basal zone (b) or supporting cell layer (s) (C), whereas NCAM is expressed in both the apical and basal zones of the VNE (D).E–G, Micrographs showing expression of OCAM (E), NCAM (F), and Goα (G) proteins in the adult mouse AOB. E and F are different images from a double-stained section. G is a section adjacent toE and F. Dorsal is at thetop; rostral is at the left. OCAM is expressed by a subset of vomeronasal axons that project into glomeruli in the rostral zone of the AOB (E), whereas NCAM is expressed by all vomeronasal axons (F). Complementary to OCAM, Goα is expressed in the caudal zone of the AOB (G). Scale bars: 200 μm forA, B; 20 μm for C, D; 200 μm forE–G.