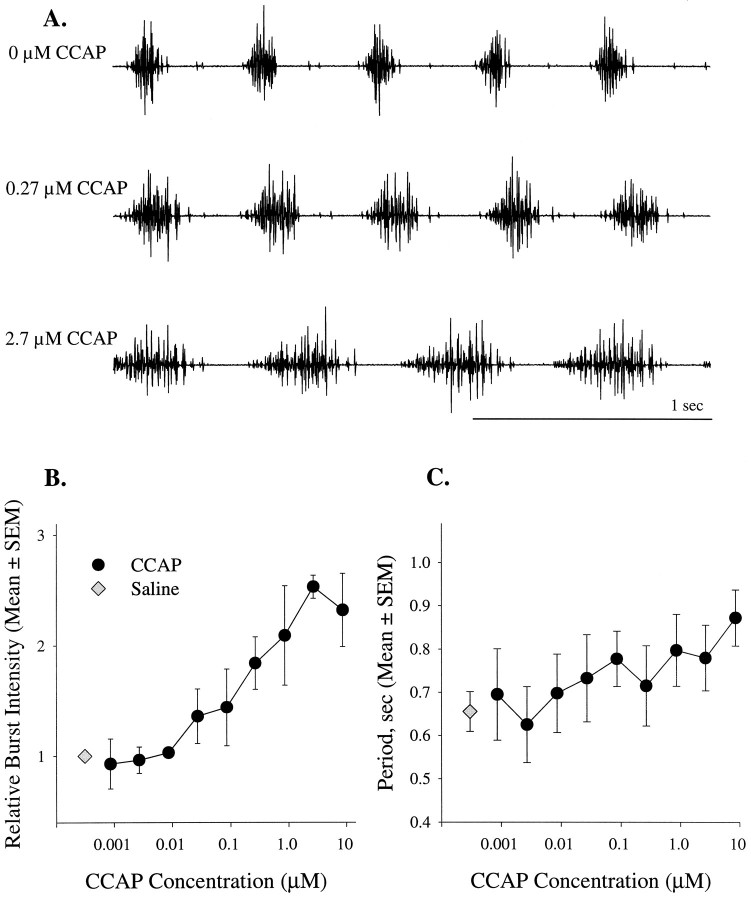
Fig. 2.
Excitation of the swimmeret motor pattern by CCAP was dose-dependent. A, Recordings from the same PS nerve in a spontaneously active preparation bathed in different concentrations of CCAP. B, When applied to active preparations, CCAP (•) increased the intensities of bursts of impulses in swimmeret neurons. Intensity was measured by integrating each burst and measuring the area circumscribed by the integral. These areas were normalized to the mean area of bursts produced spontaneously in saline (⋄) (n = 4 experiments).C, In these same preparations CCAP did not alter the period significantly.