Fig. 4.
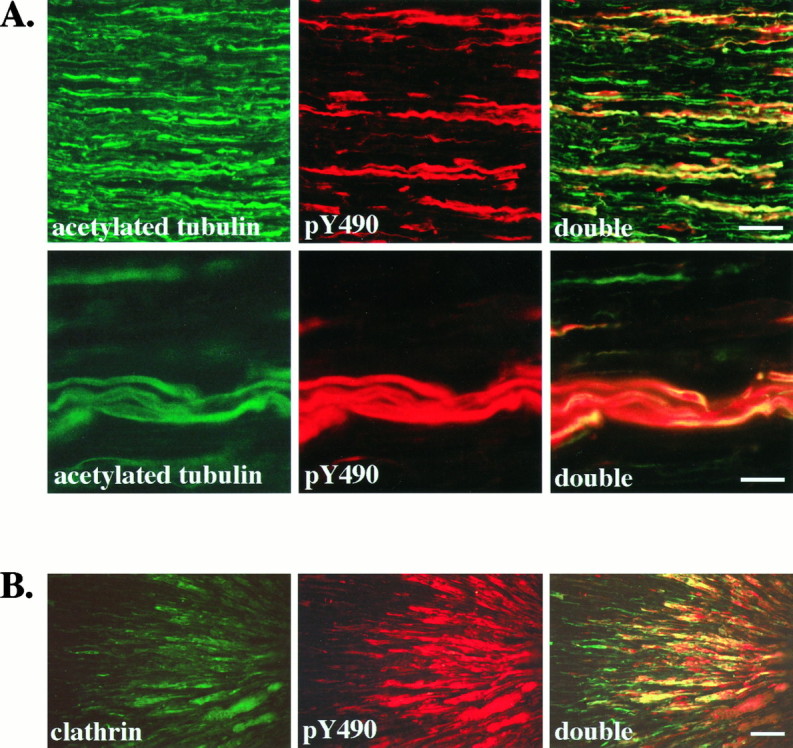
Activated Trk receptors are confined to axons in the sciatic nerve and accumulate distal to a ligation.A, Longitudinal sections of adult rat sciatic nerve were immunostained with anti-acetylated α-tubulin (acetylated tubulin) and anti-pY490 (pY490), as described, and viewed with fluorescence optics. Double labeling is shown in sections viewed with both fluorescein and rhodamine filters (double). All axons in the sciatic nerve are labeled by the acetylated tubulin antibody. In contrast, fewer axons are stained by anti-pY490. Colocalization is apparent as yellow in the double panels, demonstrating that pY490 labels only a subset of axons. Another field viewed at higher magnification (second row) shows that the anti-pY490 staining colocalizes with the acetylated tubulin staining, verifying that the pY490 immunostaining is present in axons of the sciatic nerve. Scale bars: First row, 50 μm; second row, 25 μm.B, The sciatic nerve of an adult rat was ligated ∼2 cm from the gastrocnemius muscle to interrupt vesicular transport. At 24 hr after ligation the nerve was harvested, and longitudinal sections of the nerve were immunostained with an antibody to the coated vesicle protein, clathrin and anti-pY490. The portion of nerve distal to the ligation site is shown with the ligation site to theright. Clathrin immunostaining shows accumulation of clathrin in axons on the distal side of the ligation (clathrin). Phosphorylated Trks, as shown by pY490 immunostaining, also accumulate on the distal side of the ligation (pY490). Costaining shows that phosphorylated Trks colocalize with clathrin (double). Scale bar, 50 μm.
