Fig. 2.
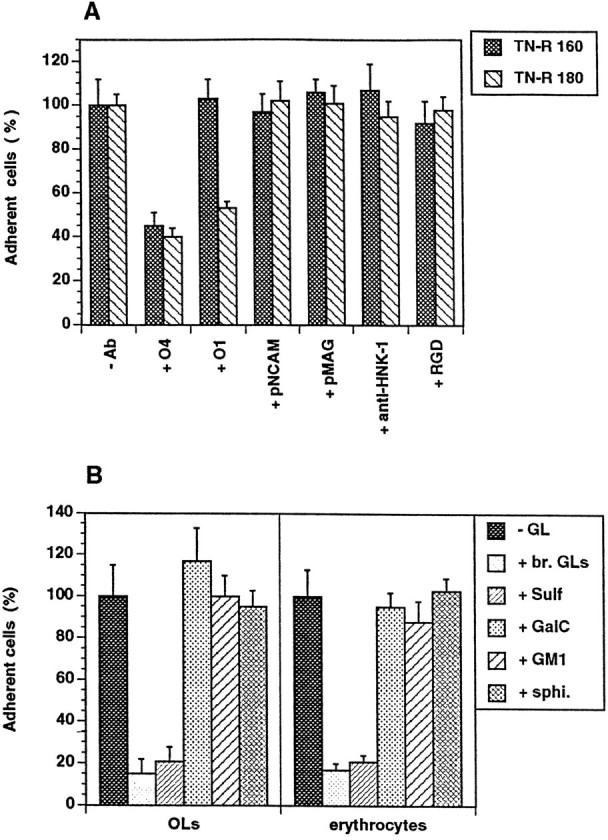
Effect of antibodies to OL surface molecules and RGD-containing peptide (A) and different polar GLs (B) on cell attachment to TN-R substrates.A, OLs were plated onto TN-R 160 or TN-R 180 either in the absence (−Ab) or presence of monoclonal antibodies to surface membrane GLs (+ O4, + O1, 100 μg/ml), polyclonal antibodies to NCAM (+ pNCAM, 50 μg/ml) and MAG (+ pMAG, 50 μg/ml), rat monoclonal antibody to the L2/HNK-1 carbohydrate (+ anti-HNK-1, 100 μg/ml), or RGD-containing peptide (+ RGD, 50 μg/ml). B, TN-R 160 substrates were preincubated in the absence (−GL) or presence of a polar GL fraction from adult mouse brain (+ br. GLs, 20 μg/ml), Sulf (+ Sulf, 5 μg/ml), GalC (+ GalC, 10 μg/ml), monosialoganglioside (+ GM1, 10 μg/ml) and sphingosine (+ sphi., 5 μg/ml), and OLs (left panel), or erythrocytes (right panel) were plated onto the substrates. The number of adherent cells after 1 hr of incubation in the absence of additives was set as 100%. Values represent the mean ± SD of four (for O4 antibody, Sulf, GalC, GM1, and sphingosine) and two (for the other antibodies, RGD-containing peptide and br. GLs) independent experiments performed in triplicate and related to the values in the absence of additives (100%).
