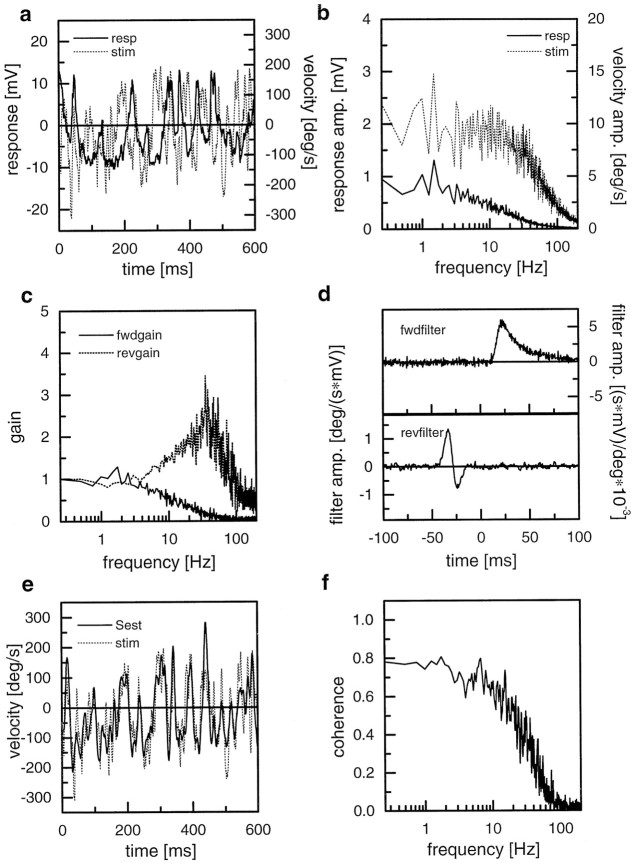
Fig. 2.
Reverse reconstruction technique exemplified on a recording from an HS-cell. a, Stimulus and response trace from an individual episode of the experiment. b, Amplitude spectra of the stimulus and the response. c, Forward and reverse gain between stimulus and response as calculated by the ratio of the cross-correlation and the respective autocorrelation (see Materials and Methods for details). d, Impulse responses of the forward and reverse filters. e, Identical stimulus segment as in a, but shown along with the estimated stimulus as calculated by convolving the response with the reverse filter. f, Coherence function between stimulus and response. This can also be understood as the forward gain between stimulus and estimated stimulus.