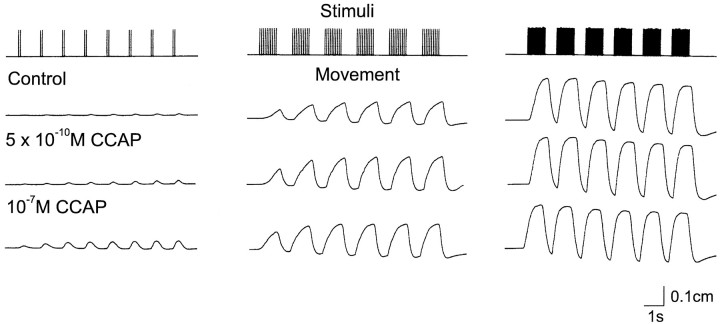
Fig. 7.
Effects of CCAP on LP-innervated muscles. The cpv4 and cpv6 muscles with attached nerves were placed in a small dish and attached to a movement transducer. A suction electrode was used to stimulate the motor nerve at 2 spikes every 1.5 sec, 10 spikes every 2 sec, and 20 spikes every 1.8 sec. The top trace shows the stimulus pattern used. The next three traces are movement recordings of the muscle in response to the stimulus indicated in thetop panel in control saline and in the presence of CCAP at the indicated concentrations. The preparation was washed for 2 hr between the application of 5 × 10−10mCCAP and that of 10−7m CCAP. During that time, it returned to control levels (not shown). After more than 90 min of washing after the treatment with 10−7mCCAP, the preparation had not completely returned to control values (not shown). The slight downward slope of the baseline seen at high stimulus frequencies is a result of the elastic properties of the movement transducer at the upper portion of its operating range.